Git
Software code version control
1 What is Git
- what? git is a version control system (The git official repo)
- for what? git is used for source code management
- how? commits are snapshots, not diffs! (The Git Object Model) and (Git Internals - Git Objects)
- where? git is a key-value store (Key Value Store Concept)
In many ways you can just see git as a filesystem—it’s content-addressable, and it has a notion of versioning, but I really designed it coming at the problem from the viewpoint of a filesystem person (hey, kernels is what I do), and I actually have absolutely zero interest in creating a traditional SCM system.
📘 Git Git is a version control system (also called a source control system) that allows programmers and other people working with text files to coordinate changes while working independently.
Git also supports binary assets such as pictures, but those formats don’t support the line-by-line version management that makes version control really powerful.
2 Key-ideas
- Git stores unique content and no duplicates
- Each key-value pair entry contains a unique hash as a key: SHA-ID.
- There are only three types of values:
- blobs for files
- tree for directories
- commit for commit messages
- commit message
- author, including a timestamp
- committer, including a timestamp
- reference to parent commit
3 git is immutable
Immutable object In object-oriented and functional programming, an immutable object is an object whose state cannot be modified after it is created. This is in contrast to a mutable object, which can be modified after it is created (from Wikipedia).
So, what does immutable snapshots refer to? In Git, all commits are immutable snapshots of your project (ignored files excluded) at a specific point in time.
This means that each and every commit contains a unique representation of your entire project, not just the modified or added files (deltas), at the time the commit was created. Apart from the actual files, each commit is also infused with relevant metadata; all of which is immutable!
check oot this article for more info about immutability
4 Install git linux
Debian / Ubuntu / Mint apt-get
Git packages are available via apt, go to terminal and from your shell, install Git using apt-get:
Verify the installation was successful by typing git –version:
Configure your Git username and email using the following commands, replacing Emma’s name with your own. These details will be associated with any commits that you create:
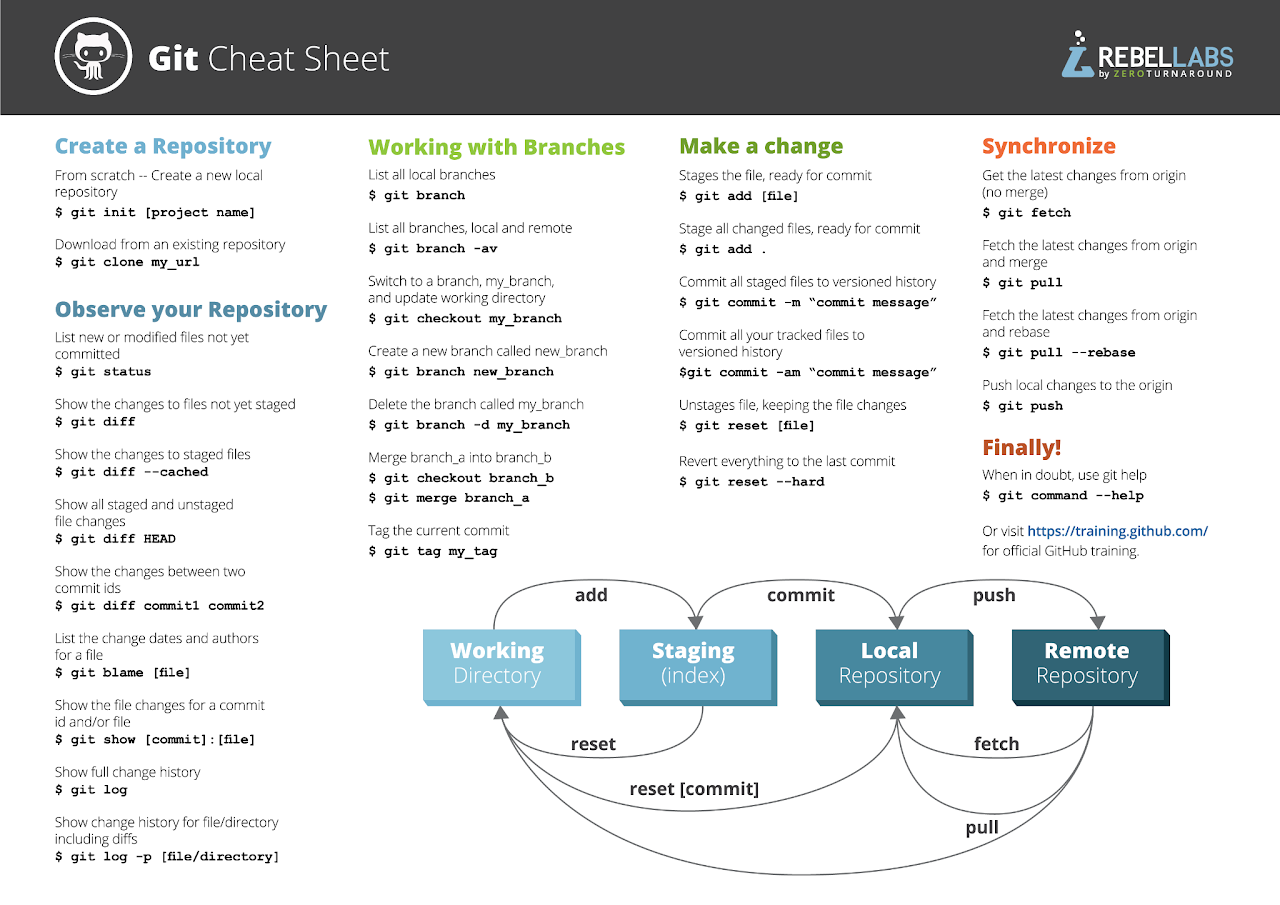
5 Git use
git init: creates or converts an existing into a new Git repository.git pull: fetches remote changes into the local clone, and merges them into the current working files.git checkout: replaces the current working files with files from a branch.git checkout --track: creates a local branch from a remote branch, links them, and replaces the current working files with files from that branch.git fetch: downloads changes from a remote repository into the local clonegit reset: makes the current branch point to some specific revision or branch.git reset --hard: makes the current branch point to some specific revision or branch, and replaces the current working files with the files from that branch.git merge: merges files from a given branch into the current branch.git push: uploads changes from local branches to the respective remote repositories.git add: puts current working files into the stage (aka index or cache)git commit: commits staged changes to a local branchgit commit -a: commits all modified files to a local branch (shorthand for “git add” and “git commit”)