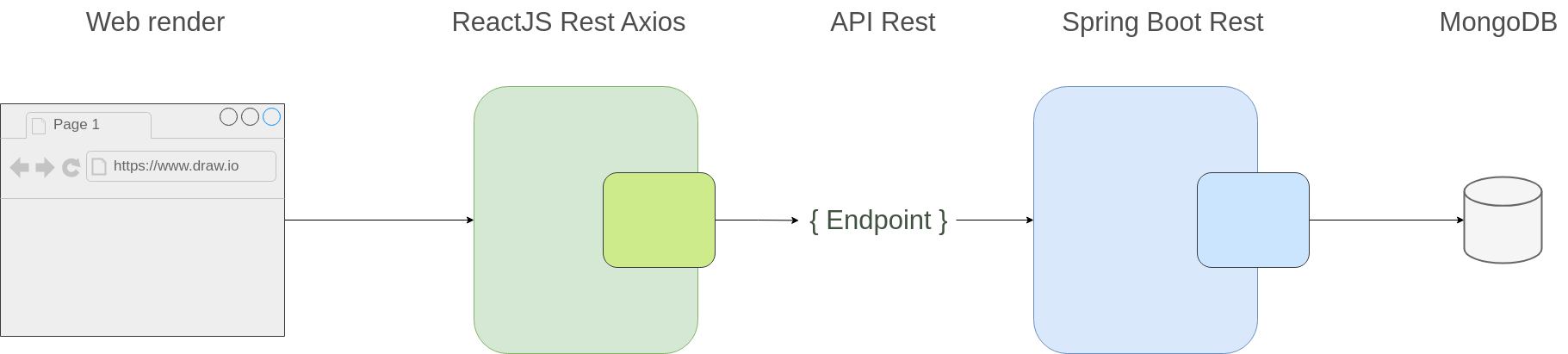
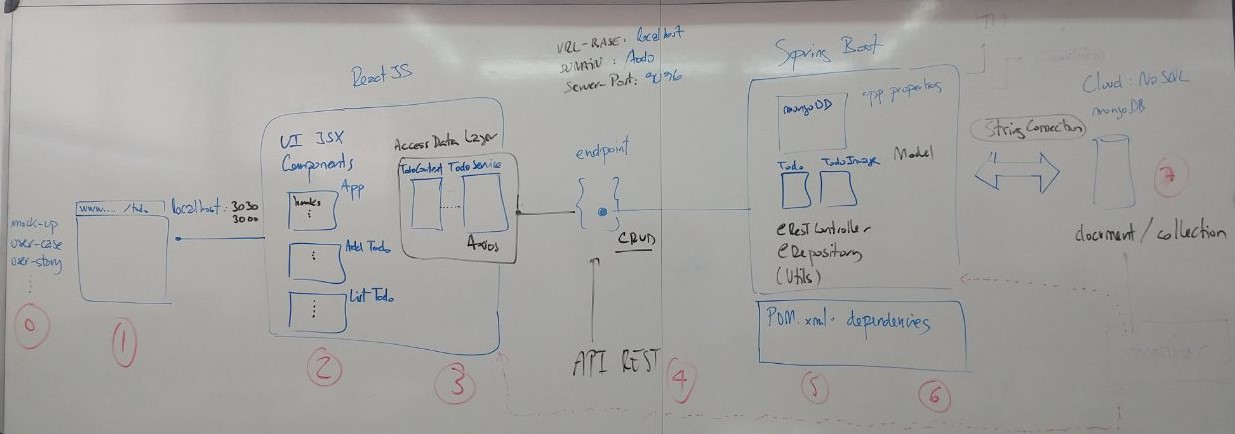
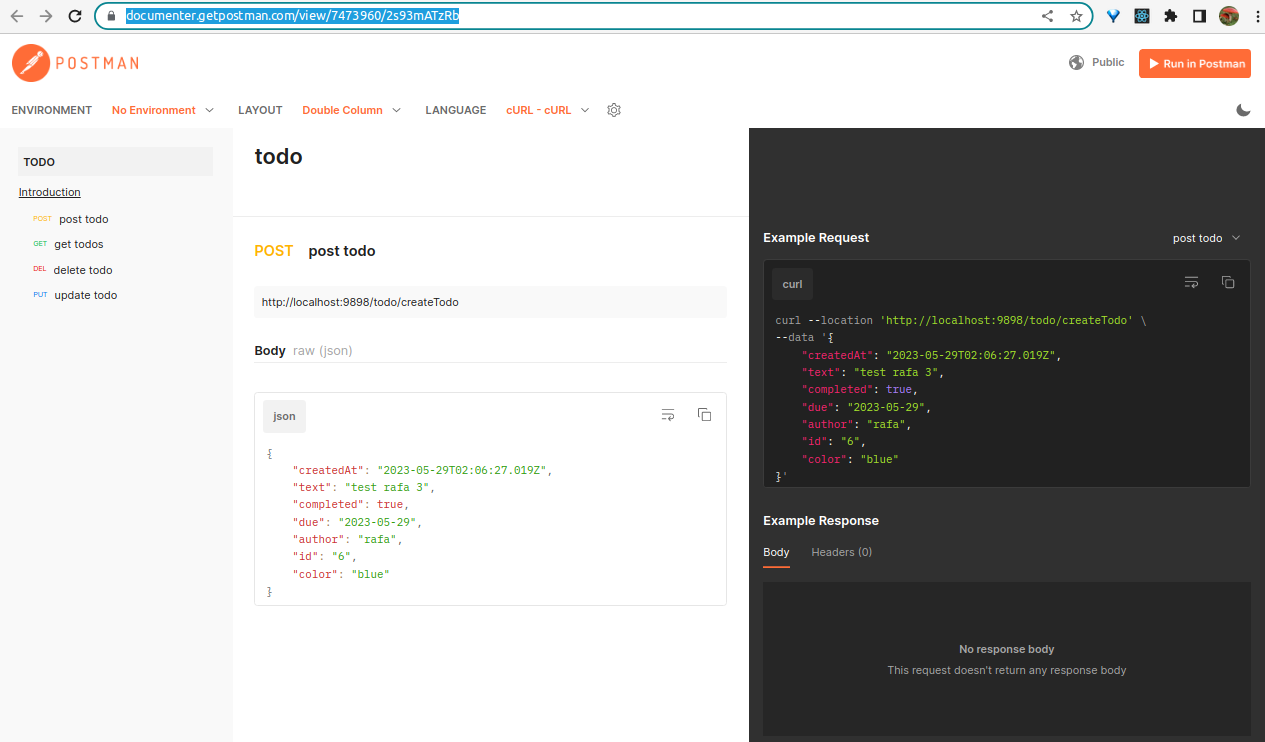
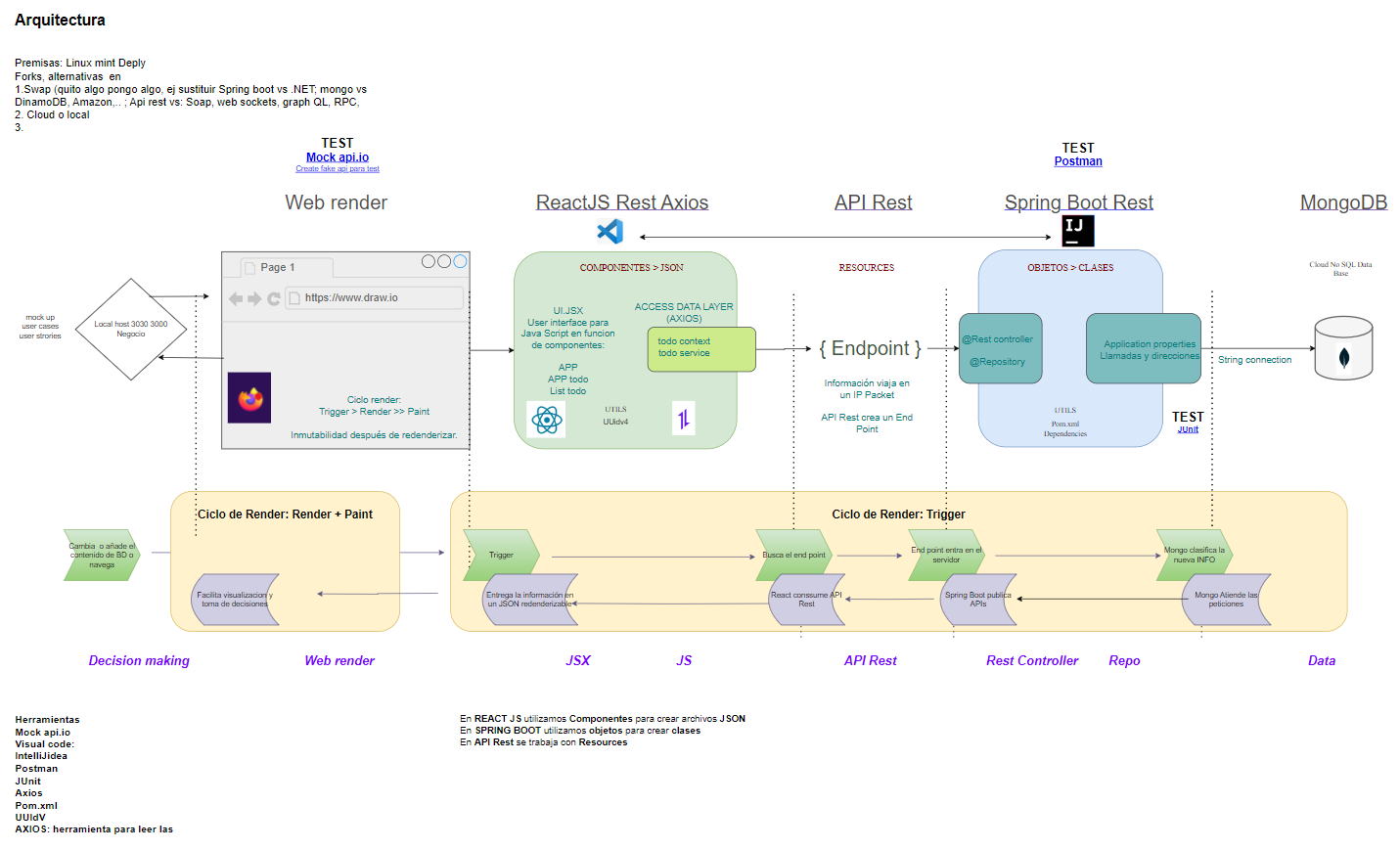
Lab#RE04-2: Spring Boot & ReactJS
ReactJS labs
📘 React JS Lab#RE04-1: Spring Boot and ReactJS
In this lab, we will be using Spring Boot server to feed our React Todo app through API Rest.
For many reasons described in the previous article the use of a React App with a Spring Boot is a very good option:
- Spring Boot: Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring based Applications that you can “just run”.
- React, the library for web and native user interfaces.
1 user-story and mock-up
1.1 Adding a task to the Todo List
As a user, I want to be able to add a task to my todo list, So that I can keep track of what I need to do.
1.1.1 Acceptance Criteria
- When I visit the todo web application, I should see an input field where I can enter a task description.
- After entering the task description, I should be able to submit it by pressing the “Add” button or hitting the Enter key.
- Once I add a task, it should appear as a new item on my todo list.
- If I enter an empty task description, the system should not allow me to add it and display an error message.
- After successfully adding a task, the input field should be cleared and ready for me to enter another task.
1.2 Deleting a Task from the Todo List
As a user, I want to be able to delete a task from my todo list, So that I can remove completed or unnecessary tasks.
1.2.1 Acceptance Criteria
- When I view the todo list, each task should have a delete button or an option to mark it for deletion.
- When I click on the delete button or mark a task for deletion, the system should remove the task from the todo list.
- If I accidentally mark a task for deletion, there should be an option to undo the deletion and restore the task to the todo list.
- The system should provide a confirmation prompt before permanently deleting a task.
- After deleting a task, the todo list should update automatically to reflect the changes.
- If the todo list is empty after deleting a task, the system should display a message indicating that there are no tasks remaining.
2 general step-by-step
To create an architecture using Spring Boot, MongoDB, and React for managing a Todo object, you can follow the steps outlined below:
2.1 Backend Architecture (Spring Boot and MongoDB):
- Set up the
Spring Bootproject:- Create a new
Spring Bootproject using your preferred IDE or use the Spring Initializr. - Include the necessary dependencies, such as
Spring Web,Spring Data MongoDB, and any additional libraries you might need.
- Create a new
- Create the
Todomodel:- Define a
Todoclass with the required fields (e.g., id, title, description, status, etc.). - Annotate the class with
@Documentto map it to aMongoDBcollection. - Use appropriate annotations like
@Id,@Field, etc., to define the mapping of the fields.
- Define a
- Create a CRUD
repository:- Create an interface that extends
MongoRepository<Todo, String>. - This
repositorywill provide the basic CRUD operations (create, read, update, delete) for the Todomodel. - Customize the repository with additional methods if needed.
- Create an interface that extends
- Create a REST
controller:- Create a controller class annotated with
@RestController. - Inject the Todo repository into the controller using
@Autowired. - Define REST endpoints using
@GetMapping,@PostMapping,@PutMapping,@DeleteMapping, etc., for CRUD operations. - Implement the necessary request mappings for each operation using the repository methods.
- Create a controller class annotated with
2.2 Frontend Architecture (React with Axios and Context):
- Set up the
Reactproject:- Create a new React project using create-react-app or your preferred method.
- Set up any additional configurations or dependencies required.
- Create a data access layer:
- Create a file for making
HTTPrequests using Axios (e.g., api.js). - Define functions for each CRUD operation, making the corresponding API calls to the backend.
- Handle responses and errors as needed.
- Create a file for making
- Set up a
context:- Create a context file (e.g.,
TodoContext.js) to manage the state and actions related to theTodoobject. - Define the necessary context provider component, which will wrap the root component.
- Implement state management functions (e.g., addTodo, deleteTodo, updateTodo) within the context provider.
- Create a context file (e.g.,
- Create
Reactcomponents:- Create React components for displaying Todo objects (e.g.,
TodoList,TodoItem,TodoAdd). - Use the context to access and modify the
Todostate and perform CRUD operations. - Render the Todo components within your application’s layout.
- Create React components for displaying Todo objects (e.g.,
With this architecture in place, your Spring Boot backend will expose RESTful endpoints for CRUD operations on the Todo object, while the React frontend can consume those APIs using Axios for data retrieval, creation, updating, and deletion.
The context-axios layer in React will handle state management and provide access to the Todo data throughout the application.
3 API rest documentation
This documentation provides an overview of the REST API endpoints implemented using Spring Boot’s Rest Controller, which will be consumed by a React JS frontend. The API endpoints allow CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations on a “todo” resource.
Published docs by Postman.
- Base URL :
http://localhost:9898 - Port: 9898
- Path:
/todo
| Operation | Query | JSON | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| GET | / |
{todo items} |
Retrieves a list of all todo items. |
| POST | /createTodo |
{todo item} body/raw/JSON |
Creates a new todo item. |
| DELETE | /?id=4 |
id as a param |
Deletes all todo items. |
| PUT | updateTodo/6 |
id as a pathvariable {todo item} body/raw/JSON |
Updates an existing todo item. |
4 step-by-step code
4.1 UML: Spring Boot - ReactJS todo
4.2 MongoDB
To connect a Spring Boot project to MongoDB, you can configure the connection string in the application.properties file.
Here’s a short intro and very general on how to do that:
First, make sure you have added the necessary dependencies for MongoDB in your pom.xml file. Include the following dependencies:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mongodb</groupId>
<artifactId>mongo-java-driver</artifactId>
</dependency>Next, open the application.properties file located in the src/main/resources directory of your Spring Boot project.
Add the following properties to the file to configure the MongoDB connection:
spring.data.mongodb.host=your-mongodb-host
spring.data.mongodb.port=your-mongodb-port
spring.data.mongodb.database=your-mongodb-databaseReplace the placeholders (your-mongodb-host, your-mongodb-port, and your-mongodb-database) with the appropriate values for your MongoDB instance.
Optionally, if your MongoDB server requires authentication, you can add the following properties to the application.properties file:
spring.data.mongodb.username=your-mongodb-username
spring.data.mongodb.password=your-mongodb-passwordReplace your-mongodb-username and your-mongodb-password with the appropriate credentials for your MongoDB instance.
MongoDB will store this kind of object:
4.3 Backend: Spring Boot todo
First, create and install dependencies (pom.xml) Spring Boot:
You may read about Spring Boot creation here
4.3.1 pom.xml
Todo.java
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.2</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>LibraryManagement</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>controllerView</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot Composition and TH</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.javafaker</groupId>
<artifactId>javafaker</artifactId>
<version>1.0.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>4.3.2 Java classes
Model:
Todo.java
package com.example.myFirstSpring.model;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import org.bson.types.Binary;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.mapping.Document;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Document(collection = "todo")
public class Todo {
@Id
private String id;
private String text;
private String author;
private LocalDate due;
private boolean completed;
//private Binary image;
}4.3.3 @CrossOrigin
By default, web browsers enforce the same-origin policy, which means that a web page can only make requests to the same origin (domain, protocol, and port) from which it was loaded.
However, in the case of a React.js app consuming a Spring Boot API running on a different origin (such as http://localhost:3000 for the React.js development server), the same-origin policy would block the API requests.
The @CrossOrigin(origins = "http://localhost:3000") annotation in the Spring Boot controller allows the API to respond to requests from the specified origin, in this case, http://localhost:3000, which is where the React.js app is hosted during development.
This enables the React.js app to successfully consume the API’s endpoints and access the necessary data.
Todo.java
TodoRepository
TodoRepository.java
package com.example.myFirstSpring.repository;
import com.example.myFirstSpring.model.Todo;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.MongoRepository;
import java.util.Optional;
public interface TodoRepository extends MongoRepository<Todo, String> {
Optional<Todo> findTodoById(String id);
void deleteTodoById(String id);
}TodoRestController
TodoRestController.java
package com.example.myFirstSpring.restcontroller;
import com.example.myFirstSpring.model.Todo;
import com.example.myFirstSpring.repository.TodoRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Optional;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/todo")
public class TodoRestController {
//here we are creating our end-point rest API
@Autowired
TodoRepository todoRepository;
//CRUD: read
@CrossOrigin(origins = "http://localhost:3000")
@GetMapping
public ResponseEntity<Iterable<Todo>> getAllTodos() {
//
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.add("operation", "findAll");
headers.add("version", "api 1.0");
headers.add("statusOperation", "success");
return ResponseEntity.accepted()
.headers(headers)
.body(todoRepository
.findAll());
}TodoRestController.java
@DeleteMapping
public ResponseEntity<Todo> deleteTodo(@RequestParam String id) {
//
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.add("operation", "deleteBook");
headers.add("version", "api 1.0");
Optional<Todo> todoFound = todoRepository.findTodoById(id);
boolean isTodo = todoFound.isPresent();
if (isTodo) {
//Optional<Book> deletedBook =
//bookservice.deleteBookById(id);
todoRepository.deleteTodoById(id);
headers.add("operationStatus", "deleted");
return ResponseEntity.accepted()
.headers(headers)
.body(todoFound
.get());
} else {
headers.add("operationStatus", "not found");
return ResponseEntity.accepted().body(null);
}
}TodoRestController.java
@PostMapping(path = "createTodo", consumes = "application/JSON")
public ResponseEntity<Todo> addTodo(@RequestBody Todo todo) {
//
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.add("operation", "createTodo");
headers.add("version", "api 1.0");
headers.add("statusOperation", "success");
Todo todoCreated = todoRepository.save(todo);
if (todoCreated != null) {
headers.add("statusOperation", "success");
return ResponseEntity.accepted()
.headers(headers)
.body(todoCreated);
} else {
headers.add("statusOperation", "not created");
return ResponseEntity.accepted().body(null);
}
}updateTodo, we could update just the completed field but to test the method we updated all the whole object.
TodoRestController.java
@PutMapping("/updateTodo/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Todo>
updateTodo(@PathVariable String id, @RequestBody Todo dataTodo) {
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.add("operation", "completeTodo");
headers.add("version", "api 1.0");
Optional<Todo> todoFound = todoRepository.findTodoById(id);
if (todoFound.isPresent()){
//System.out.println(todoFound.get()
//+ " -- " + dataTodo);
todoRepository.save(dataTodo);
headers.add("operationStatus","updated");
return ResponseEntity.accepted()
.headers(headers)
.body(todoFound
.get());
} else {
headers.add("operationStatus","not found");
return ResponseEntity.accepted()
.headers(headers)
.body(null);}
}4.4 FrontEnd: ReactJS todo
4.4.1 UI
First, the UI React .jsx components:
- TodoDomainsApp
- TodoDomainsAdd
- TodoDomainsList
TodoDomainsApp.jsx
import React, { useContext } from "react";
import TodoDomainsAdd from "../components/TodoDomainsAdd";
//import TodoList from "./TodoList";
import { TodoContext, TodoProvider } from "../service/TodoContext.js";
import {
Container,Divider
} from "semantic-ui-react";
import TodoDomainsList from "./TodoDomainsList";
const TodoDomains = () => {
const { createTodo} = useContext(TodoContext);
const handleCreateTodo = (todo) => {
createTodo(todo);
};
return (
<Container>
<br />
<h1>Todo App</h1>
<p>
A todo grid/cards with API Rest mockapi.io, with a useSate, semantic and
a service layer: axios and context. High decoupled version.
</p>
<TodoDomainsAdd onCreate={handleCreateTodo} />
<Divider />
<TodoDomainsList />
</Container>
);
};
const TodoDomainsApp = () => {
return (
<TodoProvider>
<TodoDomains />
</TodoProvider>
);
};
export default TodoDomainsApp; TodoDomainsAdd.jsx
import React from "react";
import {
Card,
Checkbox,
Button,
Form,
Divider,
Icon,
} from "semantic-ui-react";
import { v4 as uuidv4 } from "uuid";
// CRUD: create
const TodoDomainsAdd = ({ onCreate }) => {
const [text, setText] = React.useState("");
const [author, setAuthor] = React.useState("");
const [due, setDue] = React.useState("");
const handleSubmit = () => {
onCreate({
id: uuidv4(),
text: text,
author: author,
due: due,
completed: false,
});
};
return (
<>
<Form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<Form.Group>
<Card>
<Card.Content>
<Card.Header>Create Todo</Card.Header>
<Card.Meta>
</Card.Meta>
<br />
<Form.Field>
<label>Text</label>
<input
type="text"
value={text}
onChange={(e) => setText(e.target.value)}
placeholder="Enter todo text"
/>
</Form.Field>
<Form.Field>
<label>Author</label>
<input
type="text"
value={author}
onChange={(e) => setAuthor(e.target.value)}
placeholder="Enter author name"
/>
</Form.Field>
<Form.Field>
<label>Date</label>
<input
type="date"
value={due}
onChange={(e) => setDue(e.target.value)}
placeholder="Enter date to handle"
/>
</Form.Field>
<Divider />
<Form.Field>
<Checkbox label="use fetch/axios" />
</Form.Field>
<Divider />
<Button>Add Todo</Button>
</Card.Content>
<Card.Content extra>
<a>
<Icon name="time" />
UTC Central
</a>
</Card.Content>
</Card>
</Form.Group>
</Form>
</>
);
};
export default TodoDomainsAdd;TodoDomainsList.jsx
import {
Card,
Checkbox,
Button
} from "semantic-ui-react";
// CRUD: read and create list
import { TodoContext } from "../service/TodoContext.js";
import React, { useContext } from "react";
// UpdateTodo Component
const UpdateTodo = ({ todo }) => {
const { updateTodo } = useContext(TodoContext);
const handleUpdateTodo = () => {
updateTodo(todo);
};
return (
<Checkbox toggle checked={todo.completed} onChange={handleUpdateTodo} />
);
};
// DeleteTodo Component
const DeleteTodo = ({ todo }) => {
const { deleteTodo } = useContext(TodoContext);
const handleDeleteTodo = () => {
deleteTodo(todo.id);
};
return <Button onClick={handleDeleteTodo}>Delete</Button>;
};
const TodoDomainsList = () => {
const { todos } = useContext(TodoContext);
//console.log("todos list", todos);
if (todos === null) {
return <p>Loading...</p>;
}
return (
<>
<h2>Todos List</h2>
<hr />
<Card.Group>
{todos.map((todo) => (
<Card key={todo.id}>
<Card.Content>
<Card.Description>id: {todo.id}</Card.Description>
<Card.Header>{todo.text}</Card.Header>
<Card.Meta>Author: {todo.author}</Card.Meta>
<Card.Description>Due: {todo.due}</Card.Description>
<br />
<UpdateTodo todo={todo} />
</Card.Content>
<Card.Content extra>
<DeleteTodo todo={todo} />
</Card.Content>
</Card>
))}
</Card.Group>
</>
);
};
export default TodoDomainsList;4.4.2 Service
Second, the Data Access Layer with TodoService.js and TodoContex.js:
TodoService.js
import axios from "axios";
///`${API_URL}/todo`
// https://github.com/mockapi-io/docs/wiki/Quick-start-guide
// API_URL mockapi.io
//const API_BASE_URL = "https://645fbe78ca2d89f7e74cf4c9.mockapi.io/v1";
const API_BASE_URL = "http://localhost:9898";
const TodoService = {
getAllTodos: async () => {
try {
const response = await axios.get(`${API_BASE_URL}/todo`);
//console.log("retrieving todos:", response.data);
return response.data;
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error retrieving todos:", error);
throw error;
}
},
createTodo: async (todo) => {
try {
const response = await axios.post(`${API_BASE_URL}/todo/createTodo`, todo);
console.error("Data:", response.data);
return response.data;
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error creating todo:", error);
throw error;
}
},
updateTodo: async (todo) => {
try {
const response = await axios.put(`${API_BASE_URL}/todo/updateTodo/${todo.id}`, todo);
return response.data;
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error updating todo:", error);
throw error;
}
},
deleteTodo: async (todoId) => {
try {
const response = await axios.delete(`${API_BASE_URL}/todo?id=${todoId}`);
return response.data;
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error deleting todo:", error);
throw error;
}
},
};
export default TodoService;TodoContext.js
import React, { createContext, useState, useEffect } from "react";
import TodoService from "./TodoService";
const TodoContext = createContext();
const TodoProvider = ({ children }) => {
const [todos, setTodos] = useState([]);
//
useEffect(() => {
fetchTodos();
}, []);
//
const fetchTodos = async () => {
try {
const todos = await TodoService.getAllTodos();
setTodos(todos);
//console.log("todos:", todos);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error fetching todos:", error);
}
};
//
const createTodo = async (todo) => {
try {
const createdTodo = await TodoService.createTodo(todo);
setTodos((prevTodos) => [...prevTodos, createdTodo]);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error creating todo:", error);
}
};
const updateTodo = async (todoToUpdate) => {
try {
const updatedTodo = {
...todoToUpdate,
completed: !todoToUpdate.completed,
};
await TodoService.updateTodo(updatedTodo);
setTodos((prevTodos) => {
const updatedTodos = [...prevTodos];
const todoIndex = updatedTodos.findIndex(
(todo) => todo.id === updatedTodo.id
);
updatedTodos[todoIndex] = updatedTodo;
return updatedTodos;
});
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error updating todo:", error);
}
};
//
const deleteTodo = async (todoId) => {
try {
await TodoService.deleteTodo(todoId);
setTodos((prevTodos) => prevTodos.filter((todo) => todo.id !== todoId));
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error deleting todo:", error);
}
};
//
return (
<TodoContext.Provider value={{ todos, createTodo, updateTodo, deleteTodo }}>
{children}
</TodoContext.Provider>
);
};
export { TodoContext, TodoProvider };
5 Versions
| Code Version | Commit | Folder-Tree | Screeshoots |
|---|---|---|---|
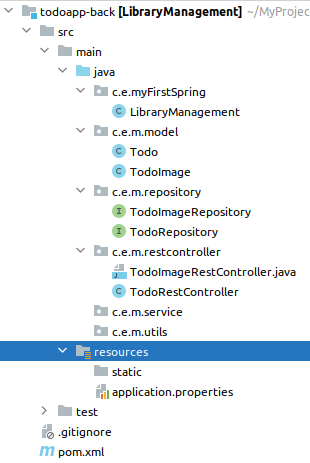
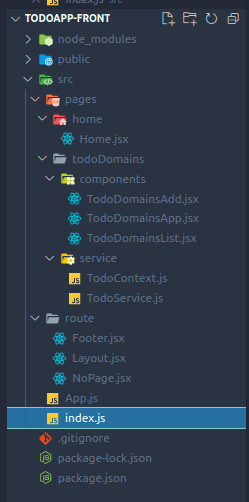
| todoApp-server 0.1 | ToDo: Just a refactored draft, only findAll works - todoApp-Back 0.1 | folder-tree Spring Boot, IntellIJIdea | - |
| todoApp-front 0.1 | ToDo: Just a refactored draft, only findAll works - todoApp-Front 0.1 | folder-tree ReactJS, Visual Code | - |
| todoApp-server 0.2 | ToDo: all operations CRUD working todoApp-Back 0.2 | - | - |
| todoApp-front 0.2 | ToDo: all operations CRUD working todoApp-Front 0.2 | - | 1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5 - 6 - 7 - 8 - 9 - 10 - 11 |
| todoApp 0.3 | Pending task: create .jsx/.js component/context/axios to upload images, spring boot @RestController done: TodoImageRepository, TodoImage, TodoImageRestController |
- | - |