Observer
Java Fundamentals and Patterns
1 Definition
The observer pattern is a design pattern in computer programming and Java that is used to notify one or mutiple objects of changes to another object.
This pattern is useful when you have a one-to-many relationship and when the state of “the one” object has to be notified in the clases that conform “the many” objects. Each object of “the many” part will be notified of changes to “the one” object.
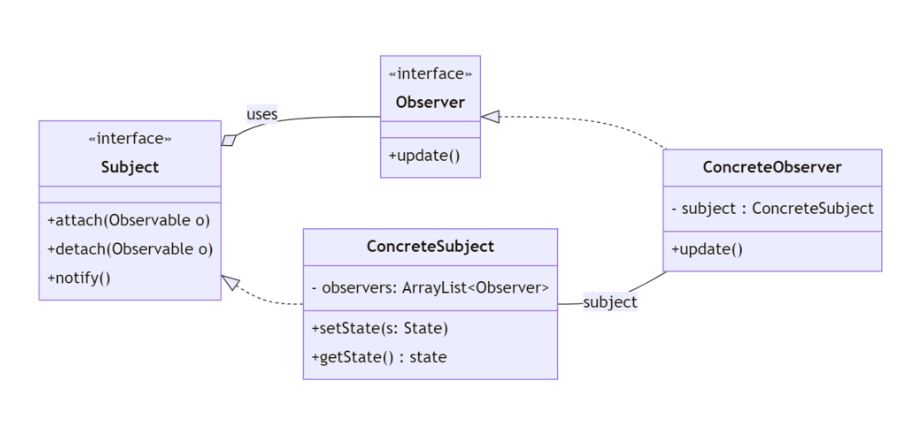
The observer pattern is usually implemented by creating an interface or an abstract class:
2 Example: Weather
Here is an example of implementation of the observer pattern step by step:
- Create the interface
Observer:
- Create the interface
Subject:
public interface Subject {
void attach(Observer observer);
void detach(Observer observer);
void notifyObservers();
}- Create a class
WeatherDatawhich implements theSubjectinterface:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class WeatherData implements Subject {
private List<Observer> observers = new ArrayList<>();
private double temperature;
public void attach(Observer observer) {
observers.add(observer);
}
public void detach(Observer observer) {
observers.remove(observer);
}
public void notifyObservers() {
for (Observer observer : observers) {
observer.update();
}
}
public void setTemperature(double temperature) {
this.temperature = temperature;
this.notifyObservers();
}
public double getTemperature() {
return temperature;
}
}- Create the
TemperatureDisplayclass which implements theObserverinterface:
public class TemperatureDisplay implements Observer {
private WeatherData weatherData;
public TemperatureDisplay(WeatherData weatherData) {
this.weatherData = weatherData;
weatherData.attach(this);
}
public void update() {
System.out.println("Temperature: " + weatherData.getTemperature());
}
}- Use the WeatherData class to notify the Observers:
WeatherData weatherData = new WeatherData();
TemperatureDisplay temperatureDisplay = new TemperatureDisplay(weatherData);
weatherData.setTemperature(27.5);The example demonstrates how to implement the Observer pattern in Java, where the WeatherData class acts as the Subject and the TemperatureDisplay class acts as the Observer.
The WeatherData class maintains a list of Observers and provides methods for attaching and detaching Observers, as well as for notifying Observers when the temperature changes. The TemperatureDisplay class receives updates from the WeatherData class and displays the temperature on the console.
When the temperature is set in the WeatherData class, it calls the notifyObservers() method which in turns calls the update() method of all the Observers. The TemperatureDisplay class receives the update and retrieves the temperature from the WeatherData instance and displays it on the console.
This pattern allows for a loosely coupled system, where the WeatherData class does not need to be aware of the existence of the TemperatureDisplay class and vice versa. The TemperatureDisplay class can be added or removed from the observer list without affecting the behavior of the WeatherData class.