React JS: render virtual DOM
ReactJS DOM
1 Overview
📘 Virtual DOM
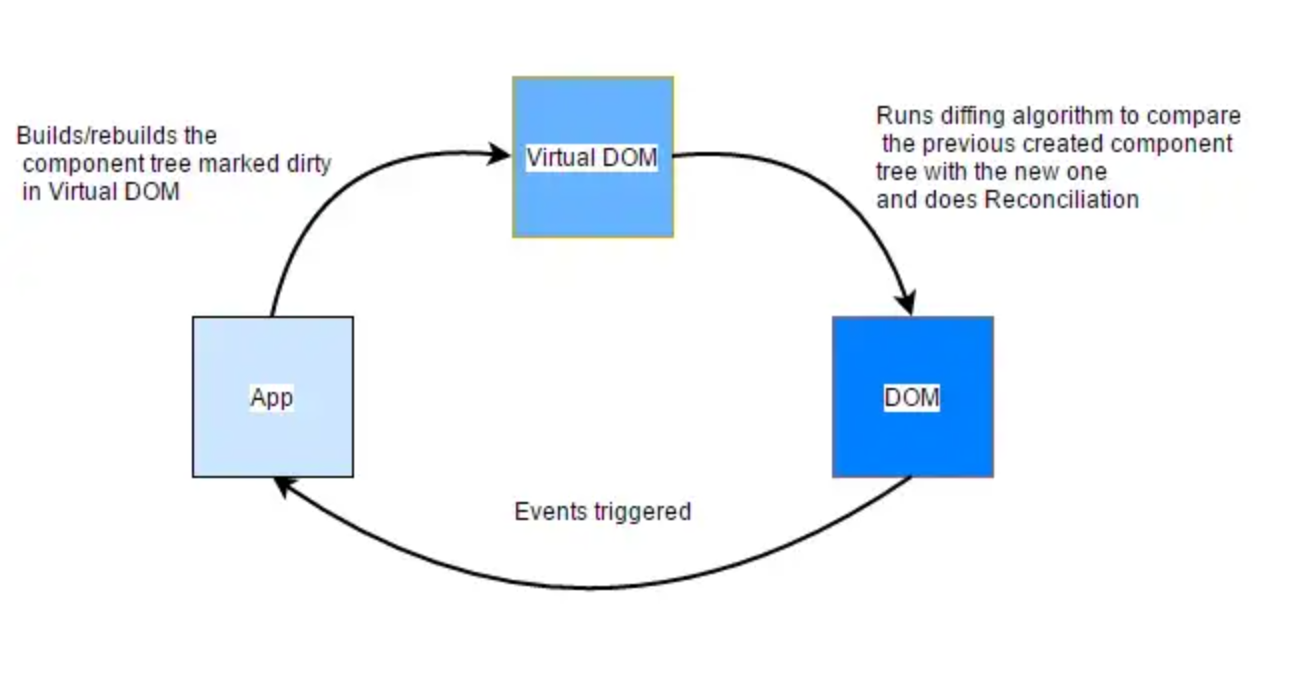
The virtual DOM VDOM is a programming concept where an ideal, or virtual, representation of a UI is kept in memory and synced with the real DOM by a library such as ReactDOM.
This process is called reconciliation.
Instead of manipulating the browser’s DOM directly, React creates a virtual DOM in memory, where it does all the necessary manipulating, before making the changes in the real browser DOM.
This approach enables the declarative API of React: you tell React what state you want the UI to be in, and it makes sure the DOM matches that state
This abstracts out the attribute manipulation, event handling, and manual DOM updating that you would otherwise have to use to build your app.
2 How Virtual-DOM and diffing works in React
How Virtual-DOM and diffing works in React
When the state of a React component changes, the component re-renders and creates a new VDOM tree. React then compares this new tree to the previous VDOM tree, using a process called “diffing.”
In React, the virtual DOM VDOM is a lightweight in-memory representation of the actual DOM. It is a tree-like structure with a hierarchy of node objects that corresponds to the structure of the DOM. Each node in the VDOM tree represents an element in the actual DOM, and has properties that correspond to the attributes and content of that element.
During the diffing process, React compares the two VDOM trees, node by node, and determines which nodes have changed, added, or removed. React then updates the actual DOM with the minimum number of changes necessary to reflect the changes in the VDOM.
This process helps to improve the performance of React applications, because it reduces the number of DOM manipulations that are required to keep the DOM up-to-date with the component’s state.
The diffing algorithm used by React is based on a concept called reconciliation. During reconciliation, React compares the VDOM nodes and their children, and determines the minimum number of steps that are needed to transform the old tree into the new tree.
This process helps to minimize the number of DOM manipulations that are required, and makes React updates faster and more efficient.
3 How it works?
When parsing JSX, React uses its internal reconciler, called the Reconciler.
Reconciler works to convert JSX syntax into function calls that create React elements.
These elements describe the desired structure and properties of UI components.
React then uses these elements to build a virtual representation of the DOM, known as the “Virtual DOM.”
The Reconciler is responsible for comparing the previous and new versions of the Virtual DOM. It identifies the specific changes needed to update the real DOM efficiently. This process is known as “reconciliation” or “diffing.”
During reconciliation, the Reconciler examines the differences between the previous and new Virtual DOM representations and calculates the minimal set of changes required.
It determines which parts of the real DOM need to be added, removed, or modified to reflect the updated component state.
Once the necessary changes are identified, the Reconciler applies them to the real DOM, selectively updating only the affected elements.
This ensures that the actual browser DOM reflects the new component state accurately. The updated content is then rendered on the screen.
By using this approach, React optimizes performance by minimizing direct interactions with the browser DOM and only updating the necessary parts.