Spring Boot: JPA Mappings
Spring Boot JPA Relationships, Mappings, Inherence and Queries
📘 JPA Mappings and relationships
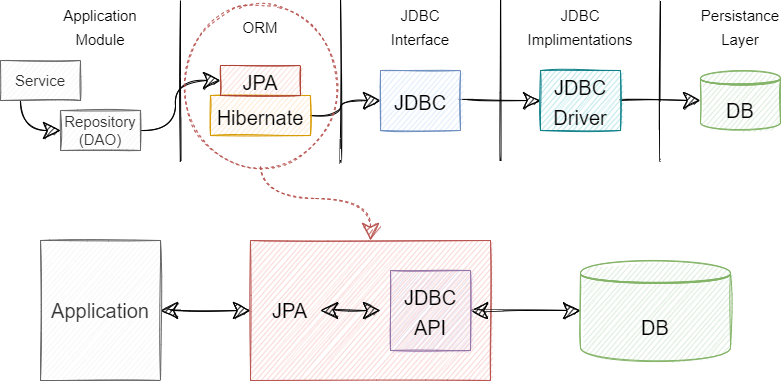
Spring Boot provides an implementation of the Java Persistence API (JPA) to simplify database access: ORM (Object-Relational Mapping)
In JPA, entity classes represent tables in the database, and relationships between entities are mapped using annotations.
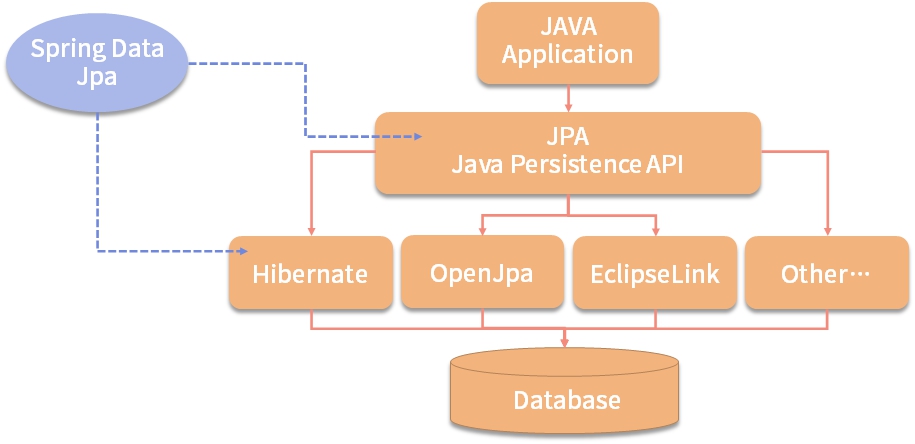
1 JPA Implementations: ORM
OpenJPA, Hibernate, and EclipseLink are all popular ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) frameworks that provide implementations of the Java Persistence API (JPA).
These frameworks simplify database access and management by mapping Java objects to database tables, and they provide features to optimize database performance and reduce the amount of boilerplate code required to interact with the database.
OpenJPAis an Apache project that provides a lightweight, high-performance implementation of JPA.Hibernateis a popular ORM framework that’s widely used in Spring Boot applications. It provides a rich set of features and has excellent community support.EclipseLinkis an open-source JPA implementation that’s known for its performance and flexibility, and it’s frequently used inJava EEapplications.
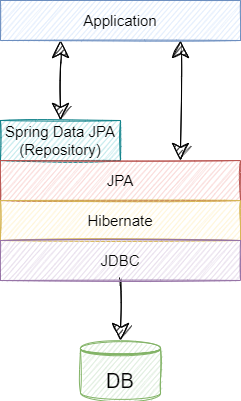
2 ORM: Hibernate
Hibernate is a popular ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) framework that provides a powerful implementation of JPA. It’s widely used in Spring Boot applications to simplify database access and management.
Hibernate uses annotations and XML configurations to map Java objects to database tables, and it provides several features to simplify CRUD (Create, Read, Update, and Delete) operations on the database.
Hibernate also provides support for caching, lazy loading, and transaction management, which can help you optimize the performance of your application.
Spring Boot and Hibernate provide a powerful combination of tools for building Java-based web applications that interact with databases.
By using these frameworks together, you can simplify database access, improve performance, and focus on building the core functionality of your application.
When you use Hibernate in your Spring Boot application, you can define entity classes using JPA annotations, just like you would with the standard JPA implementation provided by Spring Boot. Hibernate also provides its own set of annotations that can be used to fine-tune the behavior of the ORM framework.
For example, you can use the @GeneratedValue annotation to specify how primary keys are generated, or the @Fetch annotation to specify how data is retrieved from the database.
In addition to its rich set of features, Hibernate is also known for its excellent documentation and community support. You can find plenty of tutorials, sample code, and forums online to help you get started with Hibernate in your Spring Boot application.
3 Annotations
| Annotation | Description |
|---|---|
| @Entity | Specifies that the class is an entity and will be managed by the EntityManager. |
| @Table | Specifies the database table name for the entity. |
| @Id | Specifies the primary key field of the entity. |
| @GeneratedValue | Specifies how the primary key should be generated. |
| @Column | Specifies the database column name for a field. |
| @JoinColumn | Specifies the join column when using a relationship. |
| @OneToMany | Defines a one-to-many relationship between two entities. |
| @ManyToOne | Defines a many-to-one relationship between two entities. |
| @ManyToMany | Defines a many-to-many relationship between two entities. |
| @JoinTable | Specifies the join table for a many-to-many relationship. |
| @Embedded | Specifies that the field should be mapped as an embedded object. |
| @Transient | Specifies that the field should not be persisted to the database. |