Linux: Virtual Machines
Virtual Machines
1 What is a virtual machine
A virtual machine is a software program that emulates the functionality of a physical computer.
It allows a computer to run multiple operating systems and applications in **isolated environments>>>>>>> master, providing a level of isolation and security between them.
This allows users to run different operating systems and applications on the same physical computer, providing a level of flexibility and convenience that is not possible with a physical computer.
2 How it works
Virtual Machine (VM) is the virtualization/emulation of a computer system. Virtual machines are based on computer architectures and provide functionality of a physical computer. Their implementations may involve specialized hardware, software, or a combination.
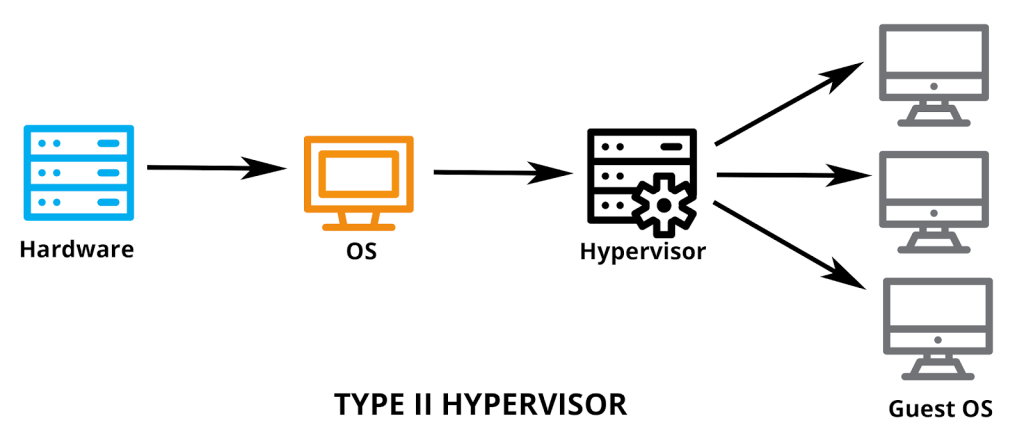
A hypervisor, also known as a virtual machine monitor or VMM, is software that creates and runs virtual machines (VMs). A hypervisor allows one host computer to support multiple guest VMs by virtually sharing its resources, such as memory and processing.
3 Benefits of hypervisors
There are several benefits to using a hypervisor that hosts multiple virtual machines:
Speed: Hypervisors allow virtual machines to be created instantly, unlike bare-metal servers. This makes it easier to provision resources as needed for dynamic workloads.Efficiency: Hypervisors that run several virtual machines on one physical machine’s resources also allow for more efficient utilization of one physical server. It is more cost- and energy-efficient to run several virtual machines on one physical machine than to run multiple underutilized physical machines for the same task.Flexibility: Bare-metal hypervisors allow operating systems and their associated applications to run on a variety of hardware types because the hypervisor separates the OS from the underlying hardware, so the software no longer relies on specific hardware devices or drivers.Portability: Hypervisors allow multiple operating systems to reside on the same physical server (host machine). Because the virtual machines that the hypervisor runs are independent from the physical machine, they are portable. IT teams can shift workloads and allocate networking, memory, storage and processing resources across multiple servers as needed, moving from machine to machine or platform to platform. When an application needs more processing power, the virtualization software allows it to seamlessly access additional machines.
4 What is Virtualbox
VirtualBox is a free and open-source virtualization platform that allows users to run multiple operating systems on a single physical computer.
It is a type of hypervisor, which means it sits between the physical hardware and the operating system, allowing multiple operating systems to run on the same hardware.
VirtualBox allows users to create and manage virtual machines, each of which can run a different operating system and be configured with its own virtual hardware. This allows users to run multiple operating systems and applications on the same computer, providing a level of flexibility and convenience that is not possible with a physical computer.
5 Step-by-step: Linux Mint
Here are the steps to create a Linux Mint virtual machine using VirtualBox on Windows:
Download and install VirtualBox on your computer.
Start VirtualBox and click the
Newbutton to create a new virtual machine.In the
Create Virtual Machinewizard, give your virtual machine a name and select Linux as the operating system type and Mint as the version.Select the amount of memory (RAM) you want to allocate to the virtual machine and click
Next.Select
Create a virtual hard disknow and clickCreate.In the C
reate a virtual hard diskwizard, selectVDI (VirtualBox Disk Image)as the disk type andDynamically allocatedas the storage type.Select the location where you want to store the virtual disk and the size of the disk, and click
Create.Click on the new virtual machine in the list and click the
Startbutton to boot the virtual machine.In the
select start-up diskwindow, select the Linux Mint ISO file that you previously downloaded from Linux Mint 21 “Vanessa” and clickStart. 9.1. If not, manually select ISO to Controller:IDE>Optic unit>Choose fileFollow the on-screen instructions to install Linux Mint on the virtual machine.
Remove the iso from the Controller:IDE>Optic unit>Choose file.
Once the installation is complete, you can use the virtual machine to run Linux Mint and any applications that are compatible with the operating system. You can also customize the virtual machine’s settings and virtual hardware to suit your needs.
Install Guest Additions: 13.1. How to Install VirtualBox Guest Additions in Linux Mint 19.1 by Linux Distro Installation Guide
Install Extension Pack: from VirtualBox that allows the VM to see the USB 3.0 on our directory.
DescriprionAllows to see on the VM the USB 3.0 provided from CIFO on our directory.
14.1. Download the VirtualBox 7.0.4 Oracle VM VirtualBox Extension Pack.
14.2. Verify the VM remains closed before the installation of the Extension Pack.
14.3. Follow the instruction of this Link