Lab#RE05-6: chat & ws: front
ReactJS labs
reactjs
lab
Lab#RE05
labs
📘 React JS Lab#RE05-6: chat & websockets
In this lab, we will be using:
- the
react-router-dom, which is a package with bindings for using React Router in web applications: websockets, provided by ReactJS framework and:- useState
- useEffect
- useContext
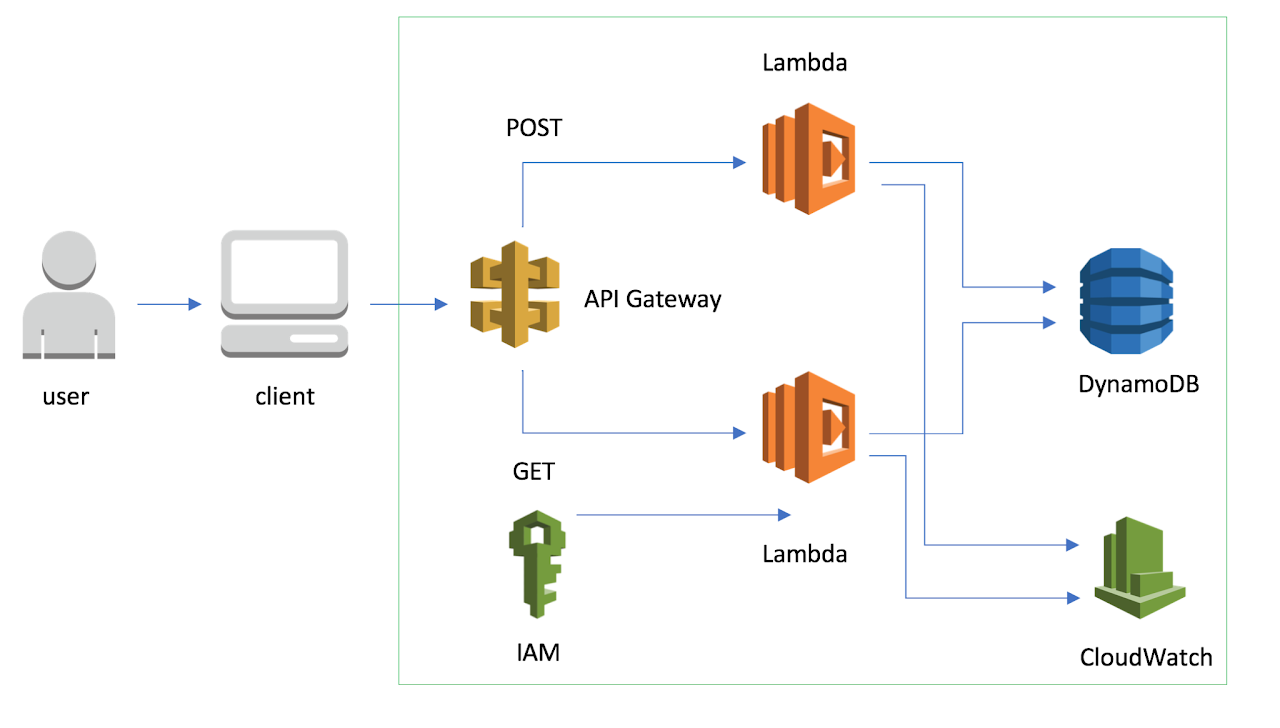
AWS, Amanzon Web Services, architecture as a server-side:- Lambda
- DynamoDB
- API Gateway
- Cloudwatch
Reference:
1 Step-by-step code
1.1 SocketProvider.js
SocketProvider.js
import { useState, useRef, useEffect, createContext } from "react";
import React from "react";
//https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/WebSocket
//https://reactjs.org/docs/context.html
//ceate context we will use as store of websockets
export const WebsocketContext = createContext(false, null, () => {});
// ..........................................ready...message...send
// Make sure to put WebsocketProvider higher up in
// the component tree than any consumers
const SocketProvider = ({ children }) => {
//two hooks to control states of connection and getting messages
const [isReady, setIsReady] = useState(false);
const [message, setMessage] = useState(null);
//hook to control websocket persistence over
// re-renders and component tree
// to any consumer
const websocket = useRef(null);
// aws endpoint
var protocol = "wss://";
//var word = "no-connection";
var word = "4rytv4evb2";
var domain = ".execute-api.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/test";
var endpoint = protocol + word + domain;
//hook to execute every render () =>
//{ function, how many renders we want}
// void > just one render at first
//[] > every new state
//[dependency] > depends on functions within dependency
useEffect(() => {
//create socket object
const socket = new WebSocket(endpoint);
//if we open, set isReady to true
socket.onopen = () => setIsReady(true);
//if we close, set isReady to false
socket.onclose = () => setIsReady(false);
//if we get a message, set message on that event (JSON)
socket.onmessage = (event) => setMessage(event.data);
websocket.current = socket;
//close socket on return, that is, useEffect may use
//this feature as optional, in this case we use it
//to clean-up and close when exit the tab
return () => {
socket.close();
};
}, []);
//create variable JSON with the 3 websocket-states we will use
//along the component tree: connection (isReady),
//get messages from server,
//sendind messages : function
const actionsWebSocket = [
isReady,
message,
//function to send ws WHEN it is called
websocket.current?.send.bind(websocket.current)
];
//ending component: we call context => WebsoockettContext
//so socket provider is a component which returns a context
//And this context goes with explicit props: actionsWebSocket
return (
<WebsocketContext.Provider value={actionsWebSocket}>
{children}
</WebsocketContext.Provider>
);
};
export default SocketProvider;1.2 Chat.jsx
1.3 ChatRoom.jsx
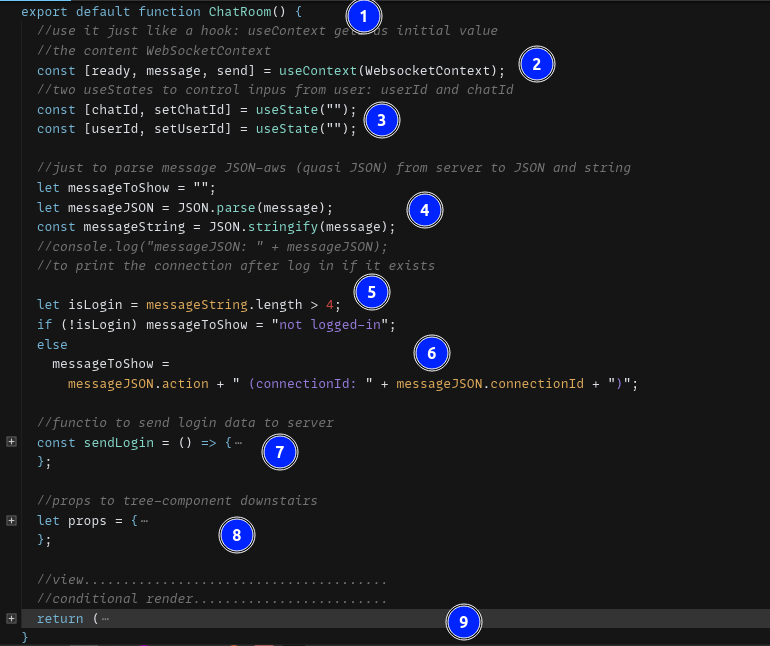
- Declare function and export
useContext: it just like a hook: useContext gets as initial valueconst [ready, message, send] = useContext(WebsocketContext);
- two
useStatesto control inpus from user: userId and chatIdconst [chatId, setChatId] = useState("");const [userId, setUserId] = useState("");
- Parse message JSON-aws (quasi JSON) from server to JSON and string
- Calculate boolean
isLogin:let isLogin = messageString.length > 4; if-elsewithisLoginto print wether the user is logged or not- function to send login data to server
- Packing
propsto tree-component downstairs - Render
ChatRoom.jsx
import React from "react";
import { useContext, useState } from "react";
import { WebsocketContext } from "./SocketProvider";
import Conversation from "./Conversation";
export default function ChatRoom() {
//use it just like a hook: useContext gets as initial value
//the content WebSocketContext
const [ready, message, send] = useContext(WebsocketContext);
//two useStates to control inpus from user: userId and chatId
const [chatId, setChatId] = useState("");
const [userId, setUserId] = useState("");
//just to parse message JSON-aws (quasi JSON)
//from server to JSON and string
let messageToShow = "";
let messageJSON = JSON.parse(message);
const messageString = JSON.stringify(message);
//console.log("messageJSON: " + messageJSON);
//to print the connection after log in if it exists
let isLogin = messageString.length > 4;
if (!isLogin) messageToShow = "not logged-in";
else
messageToShow =
messageJSON.action +
" (connectionId: " + messageJSON.connectionId + ")";
//functio to send login data to server
const sendLogin = () => {
let data = {
action: "login",
chatId: chatId,
userId: userId
};
if (ready) send(JSON.stringify(data));
};
//props to tree-component downstairs
let props = {
userId: userId,
chatId: chatId
};
//view.......................................
//conditional render.........................
return (
<>
<div>
<h3>Chat Room</h3>
<p>
Status connection: <b> {JSON.stringify(ready)}</b>
</p>
{ready && !isLogin ? (
<>
<label> UserId </label>
<input
type="text"
placeholder="Alex"
onChange={(e) => setUserId(e.target.value)}
/>
<label> ChatId </label>
<input
type="text"
placeholder="chatReactAWS"
onChange={(e) => setChatId(e.target.value)}
/>
<br />
<button onClick={sendLogin}>Enter chat room</button>
<p>
Status log in: <b> {messageToShow}</b>
</p>
</>
) : (
""
)}
{isLogin ? <Conversation {...props} /> : ""}
</div>
</>
);
}1.4 Conversation.js
- Declare function and export
useContext: it just like a hook: useContext gets as initial valueconst [ready, message, send] = useContext(WebsocketContext);
- declare
useReducerto manage conversation states - declare
useStateto manage text to print on screen from messages reducer: a reducer function calledconversationReducerthat handles different actions:- When the action type is “
send”, it creates a data object with information like action,chatId,userId, andtext. - If ready is
true, it sends the data as a string. - It then returns a new state array with a new message object appended.
- When the action type is “
receive”, it parses the message and creates a new message object with properties likeid,time,chatId,userId, andtext. - It returns a new state array with the new message object appended.
- When the action type is “
login”, it parses the message and creates a new message object with properties likeid,userId,time, andtext. - The text is
constructedusing different properties from the parsed message. - It returns a new state array with the new message object appended.
- For any other action type, it simply returns the current state unchanged.
- When the action type is “
useEffect: it runs when the message variable changes.- It checks if the message does not contain the string “
sent at”. - If it doesn’t, it parses the message JSON and checks if the action property is “
conversation”. - If it is, it dispatches a “receive” action with the message as the payload; otherwise, it
dispatchesa “login” action. - The variable
isConverastionis used to track whether the message is a conversation. - The final line logs the value of
isConverastionand message to the console.
- It checks if the message does not contain the string “
- Packing
propsto tree-component downstairs - Render
function ConversationsList
Conversation.jsx
import React from "react";
import { useContext, useState, useReducer, useEffect } from "react";
import { WebsocketContext } from "./SocketProvider";
export default function Conversation(props) {
// use it just like a hook
const [ready, message, send] = useContext(WebsocketContext);
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(conversationReducer, []);
const [text, setText] = useState("");
function conversationReducer(state, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case "send": {
let data = {
action: "conversation",
chatId: props.chatId,
userId: props.userId,
text: action.payload
};
if (ready) send(JSON.stringify(data));
return [
...state,
{
id: Date.now(),
time: Date.now(),
chatId: props.chatId,
userId: props.userId,
text: action.payload
}
];
}
case "receive": {
return [
...state,
{
id: Date.now(),
time: JSON.parse(message).time,
chatId: JSON.parse(message).chatId,
userId: JSON.parse(message).userId,
text: JSON.parse(message).text
}
];
}
case "login": {
return [
...state,
{
id: Date.now(),
userId: "status",
time: JSON.parse(message).time,
text:
JSON.parse(message).action +
" at " +
JSON.parse(message).time +
" with connection: " +
JSON.parse(message).connectionId
}
];
}
default: {
return state;
}
}
}
useEffect(() => {
var isConverastion = false;
let stringMessage = JSON.stringify(message);
if (!stringMessage.includes("sent at")) {
isConverastion = JSON.parse(message).action === "conversation";
if (isConverastion) dispatch({ type: "receive", payload: message });
else dispatch({ type: "login", payload: message });
}
console.log("isConverastion: "
+ isConverastion + " - message: " + message);
}, [message]);
let propsConversationLines = {
state: state,
userId: props.userId
};
return (
<>
<div>
<h2>Conversation</h2>
<hr />
<div
style={{
color: "black",
backgroundColor: "azure",
padding: "10px",
width: "400px",
fontFamily: "Helvetica",
fontSize: "13px"
}}
>
<ConversationsList {...propsConversationLines} />
</div>
<br />
<input
type="text"
name="content"
placeholder="say hello"
onChange={(e) => setText(e.target.value)}
/>
<button onClick={() =>
dispatch({ type: "send", payload: text })}>
{" "}
Send
</button>
</div>
</>
);
}
function ConversationsList(propsConversationLines) {
return propsConversationLines.state.map((item) => (
<>
{propsConversationLines.userId === item.userId ? (
<p
style={{
textAlign: "right"
}}
>
{item.userId}: {item.text}
</p>
) : (
<p
style={{
textAlign: "left"
}}
>
{item.userId}: {item.text}
</p>
)}
</>
));
}