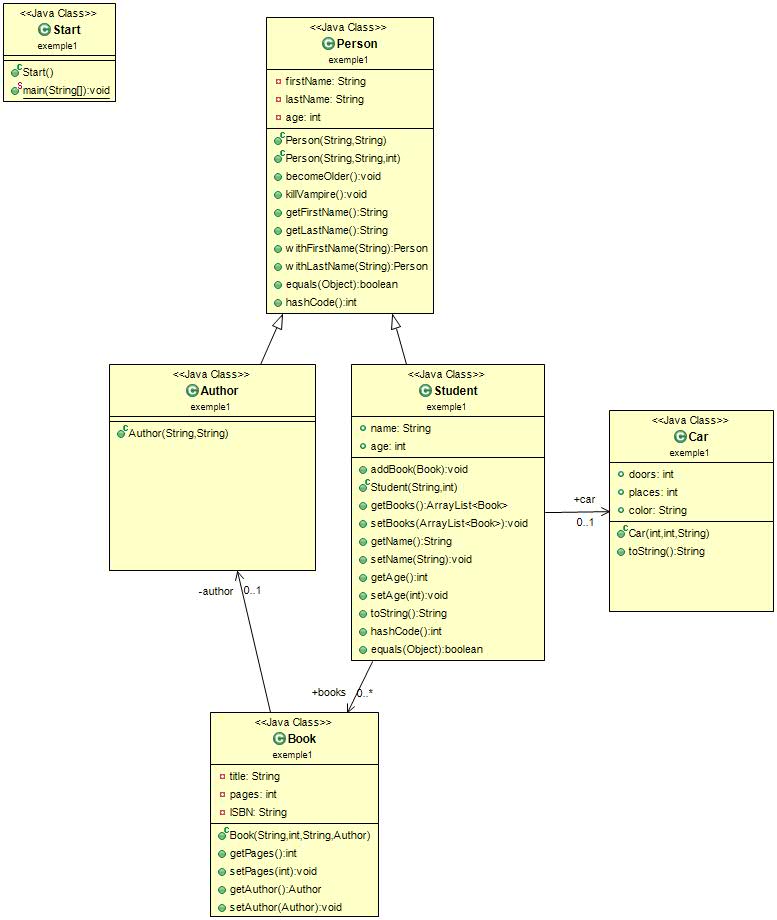
classDiagram
class Person {
-firstname: String
-lastname: String
-age: int
}
class Student {
-university: String
}
class Author {
-genre: String
}
Person --|> Student: Inheritance
Person --|> Author: Inheritance
Lab#SE00-1: Maven Person
Java SE Lab 00
javase
lab
model
composition
inherence
Java SE Lab 00 - Part 1
📘 Linux Lab#SE00-1: Person
Create a
Maven/GradleJava SE Project with theUMLand classes defined below.Add
Lombok,JUnitandFakerdependenciesRefactor: remove boilerplate code (getters, setters and so on) and work with
LombokCreate
Junittests to test objects. UseFakerto create objects:- Test
createPerson: check whether the objectPersoncreation works properly. - Test
createCar: check whether the objectCarcreation works properly. - Test
createBook: check whether the objectBookcreation works properly. - Test
createStudent: check whether the objectStudentcreation works properly - Without composition: a
Studentobject without car and books. - With composition: a
Studentobject withCarobject andBookList objects
- Test
Create
Junittests to test operations:- Test
methodsPerson: check thatPersonmethods work properly:becomeOlder(),killVampire(),withFirstName()
- Test
Improve
Car,BookandAuthorclasses with two methods each.
1 UML
classDiagram
class Student {
-university: String
-car: Car
-books: ArrayList~Book~
}
class Author {
-genre: String
-book: Book
}
class Book {
-title: String
-ISBN: String
-pages: int
-author: Author
}
class Car {
-places: int
-color: String
}
Student *-- Book: Composition
Book *-- Author: Composition
Student *-- Car: Composition
Author *-- Book: Composition
classDiagram
class Person {
-firstname: String
-lastname: String
-age: int
}
class Student {
-university: String
-car: Car
-books: ArrayList~Book~
}
class Author {
-genre: String
-book: Book
}
class Book {
-title: String
-ISBN: String
-pages: int
-author: Author
}
class Car {
-places: int
-color: String
}
Person --|> Student: Inheritance
Person --|> Author: Inheritance
Student *-- Book: Composition
Book *-- Author: Composition
Student *-- Car: Composition
Author *-- Book: Composition
2 Base Classes
2.1 Person Class
Here, the Person class represents a person with a name, address and others.
Code Person
Person.java
package exemple1;
public class Person {
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private int age;
//private boolean vampireState= true;
public Person(String firstName, String lastName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.age = 189;
}
public Person(String firstName, String lastName, int newAge) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.age = newAge;
}
public void becomeOlder() {
age = age + 5;
}
public void killVampire () {
age = -150;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public Person withFirstName(String firstName) {
return new Person(firstName, lastName);
}
public Person withLastName(String lastName) {
return new Person(firstName, lastName);
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) {
return false;
}
Person person = (Person) o;
if (firstName != null ? !firstName.equals(person.firstName) : person.firstName != null) {
return false;
}
if (lastName != null ? !lastName.equals(person.lastName) : person.lastName != null) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
public int hashCode() {
int result = firstName != null ? firstName.hashCode() : 0;
result = 31 * result + (lastName != null ? lastName.hashCode() : 0);
return result;
}
}2.2 Book Class
Here, the Book class represents a book with a title, pages and others.
Code Book
Book.java
package exemple1;
public class Book {
private String title;
private int pages;
private String ISBN;
private Author author;
public Book(String title, int pages, String iSBN, Author author) {
// super();
this.title = title;
this.pages = pages;
ISBN = iSBN;
this.author = author;
}
public int getPages() {
return pages;
}
public void setPages(int pages) {
this.pages = pages;
}
public Author getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(Author author) {
this.author = author;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book [title=" + title + ", pages=" + pages + ", ISBN=" + ISBN + "]";
}
}2.3 Student Class
Here, the Student class represents a student with a name, age and others.
Code Student
Student.java
package exemple1;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Student extends Person {
public String university;
public Car car;
public ArrayList<Book> books;
//1
//public ArrayList<Book> books = new ArrayList<Book>();
public Student(String firstName, String lastName, int age, String university) {
super(firstName, lastName, age);
this.books = new ArrayList<Book>();
}
public void addBook (Book booktoaddtoarray) {
this.books.add(booktoaddtoarray);
}
public ArrayList<Book> getBooks() {
return books;
}
public void setBooks(ArrayList<Book> books) {
this.books = books;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Student other = (Student) obj;
if (age != other.age)
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
return true;
}
result = prime * result + age;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
}
}2.4 Car Class
Here, the Car class represents a car with doors, places and other attributes.
Code Car
Car.java
package exemple1;
public class Car {
public int doors;
public int seats;
public String color;
public Car(int doors, int places, String color) {
this.doors = doors;
this.seats = seats;
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
//return "Car [toString()=" + super.toString() + "]";
return "Car [doors=" + this.doors + ", seats=" + this.seats + ", color=" + this.color + "]"
}
}