Linux: su and sudo
Bash su and sudo
📘 Linux
su and sudo are two different commands in Linux that are used to execute commands with the privileges of another user.
1 Introduction
Both su and sudo are useful tools for managing and interacting with a Linux system, but they have different uses and implications. su allows you to switch to another user account and operate as that user, while sudo allows you to execute a single command with the privileges of another user without switching to that user’s account.
sustands for switch user, and it allows you to switch to another user account and execute commands with that user’s privileges. For example, if you are currently logged in as a normal user and you want to run a command as the root user, you can use thesucommand to switch to the root user and then run the command.sudostands for superuser do, and it allows you to execute a single command with the privileges of another user, usually the root user. It is often used to execute commands that require administrative privileges, such as installing software or making system-wide configuration changes.
But in Linux Mint sudo is often considered to be a better alternative to su for several reasons, it allows you to execute a single command with administrative privileges, logs all command executions, allows for a more fine-grained control over who can execute which commands, prompts for the user’s password before execution, and is more widely used and supported in the Linux community.
2 sudo -i
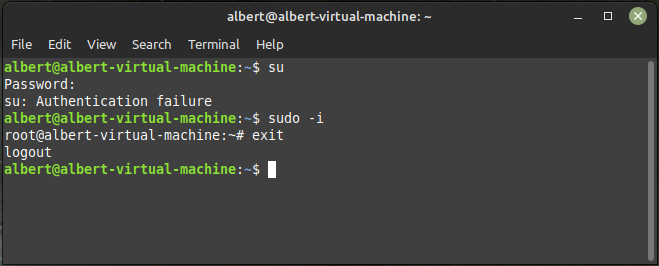
The sudo -i, The -i flag stands for initialize. command is used to execute a command or start a shell session as another user, usually the root user, with that user’s environment and privileges.
sudo -i causes the command or shell session to be executed as if the target user had logged in directly. This means that the target user’s environment variables, shell settings, and other configuration options will be applied to the command or shell session.
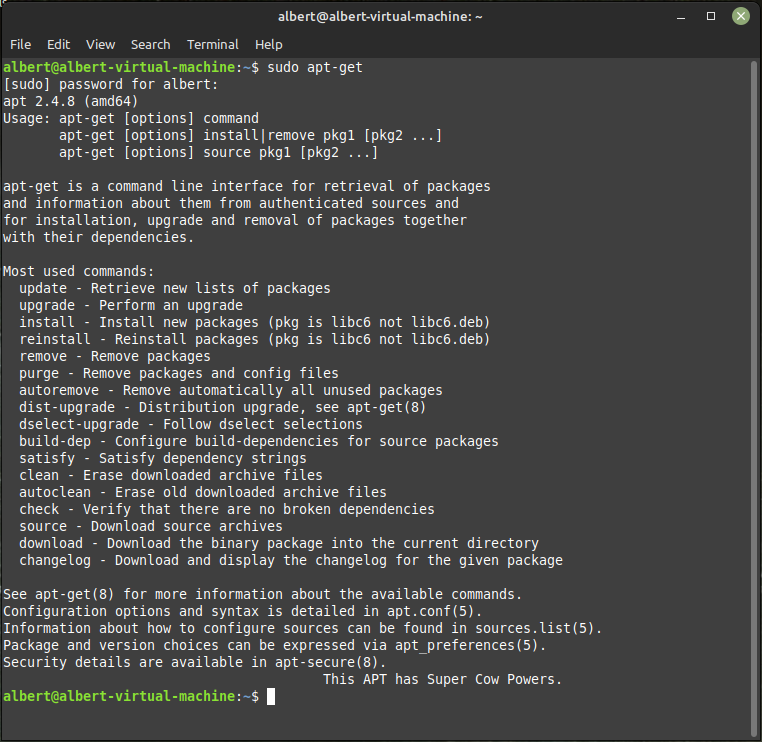
3 sudo apt-get update
apt-get is a command line interface for retrieval of packages and information about them from authenticated sources and for installation, upgrade and removal of packages together with their dependencies.
4 adduser
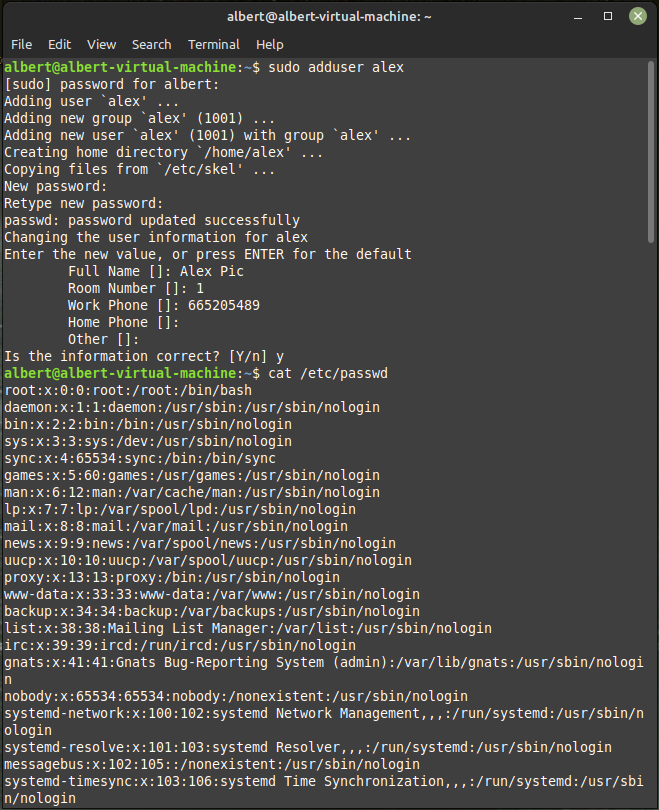
adduser: This command is used to add a new user to the system.
- For example, to add a new user with the username alex, you can use the command
sudo adduser alex. sudo userdel alex, theuserdelcommand is used to delete a user account and the user’s home directory from the system.sudo adduser alex --shell /bin/bash --gid 0, to add a new user named alex with root privileges usingsudo adduser.- To list all users on a Linux system, you can use the
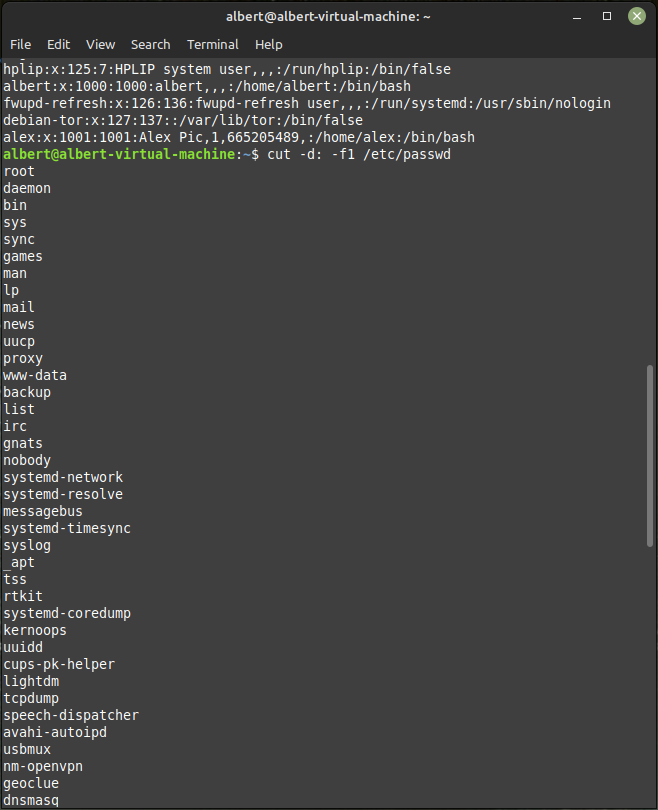
catcommand to display the contents of the/etc/passwdfile. The/etc/passwdfile contains information about all the users on the system, including their username, user ID (UID), and home directory:cat /etc/passwd - Alternatively, you can use the
cutcommand to extract the username from each line of the/etc/passwdfile:cut -d: -f1 /etc/passwd.