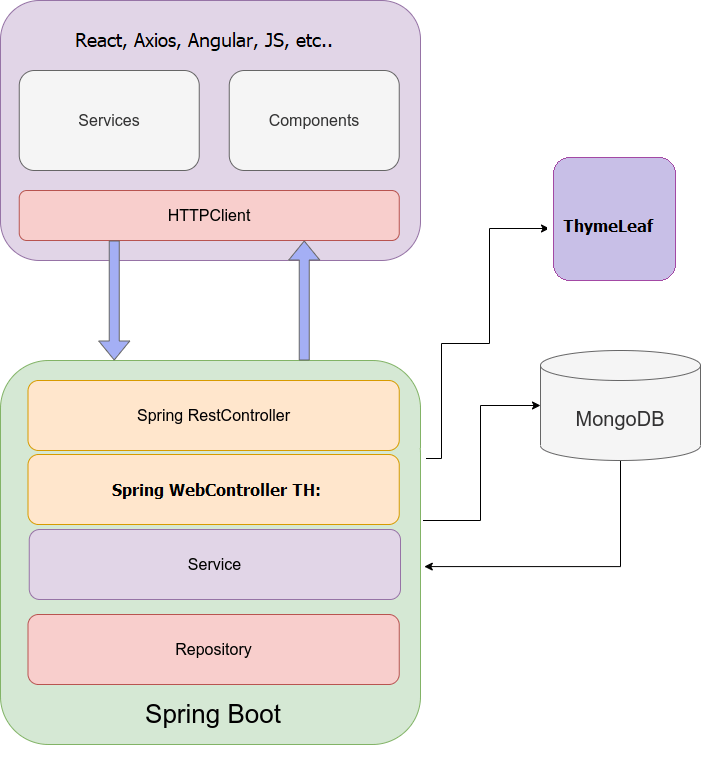
Lab#SB00-6: Rest & MongoDB
Spring Boot Library Management API Rest and NoSQL-MongoDB
📘 Spring Boot Lab#SB00-6: API Rest and NoSQL-MongoDB
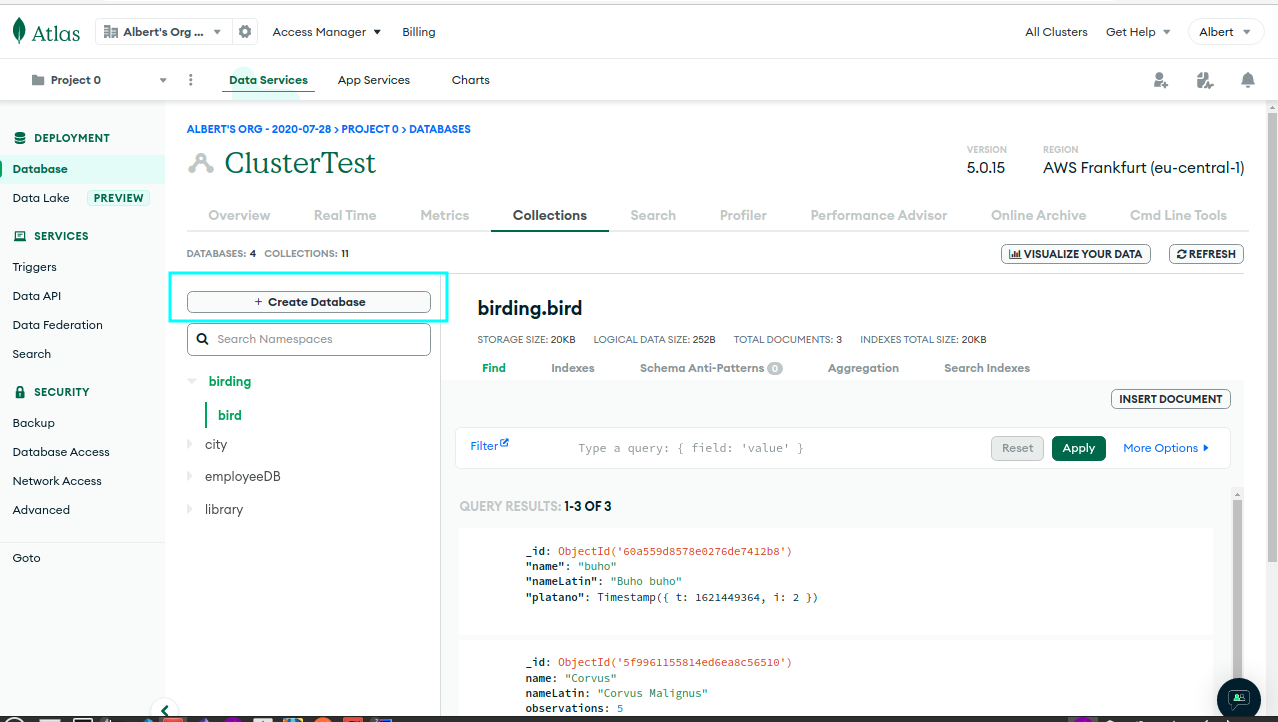
Connecting Spring Boot entity book to MongoDB Atlas can be completed in a few steps.
To connect Spring Boot entity book to MongoDB Atlas, create an account, cluster and database user on MongoDB Atlas. Add MongoDB dependency, configure application.properties and create a Book entity and repository.
Finally, use the repository to perform CRUD operations on your books collection.
1 References
2 Example: Book
To connect your Spring Boot entity book to MongoDB Atlas, you can follow these steps:
Create a
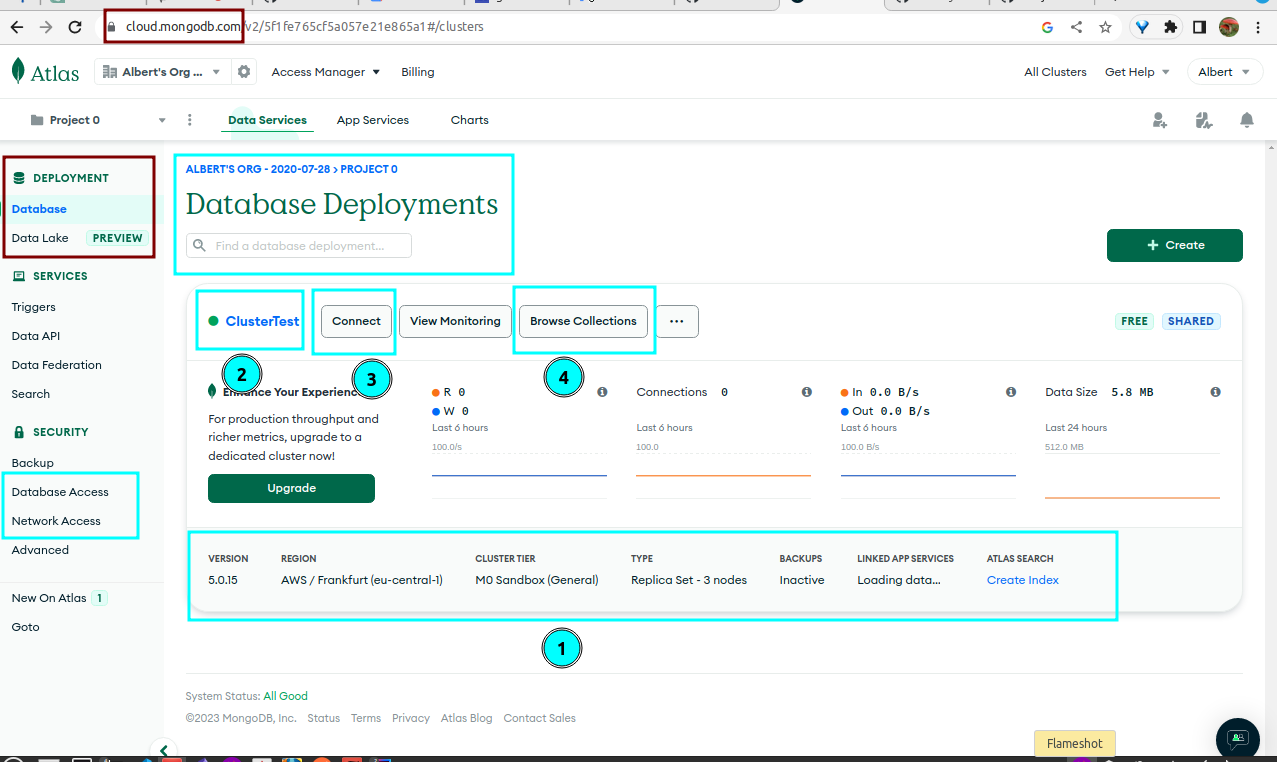
MongoDB Atlas account: First, you need to create an account onMongoDB Atlas. You can sign up for a free account with a limit of 512 MB storage.Create a new project: After logging in, create a new project and give it a name.
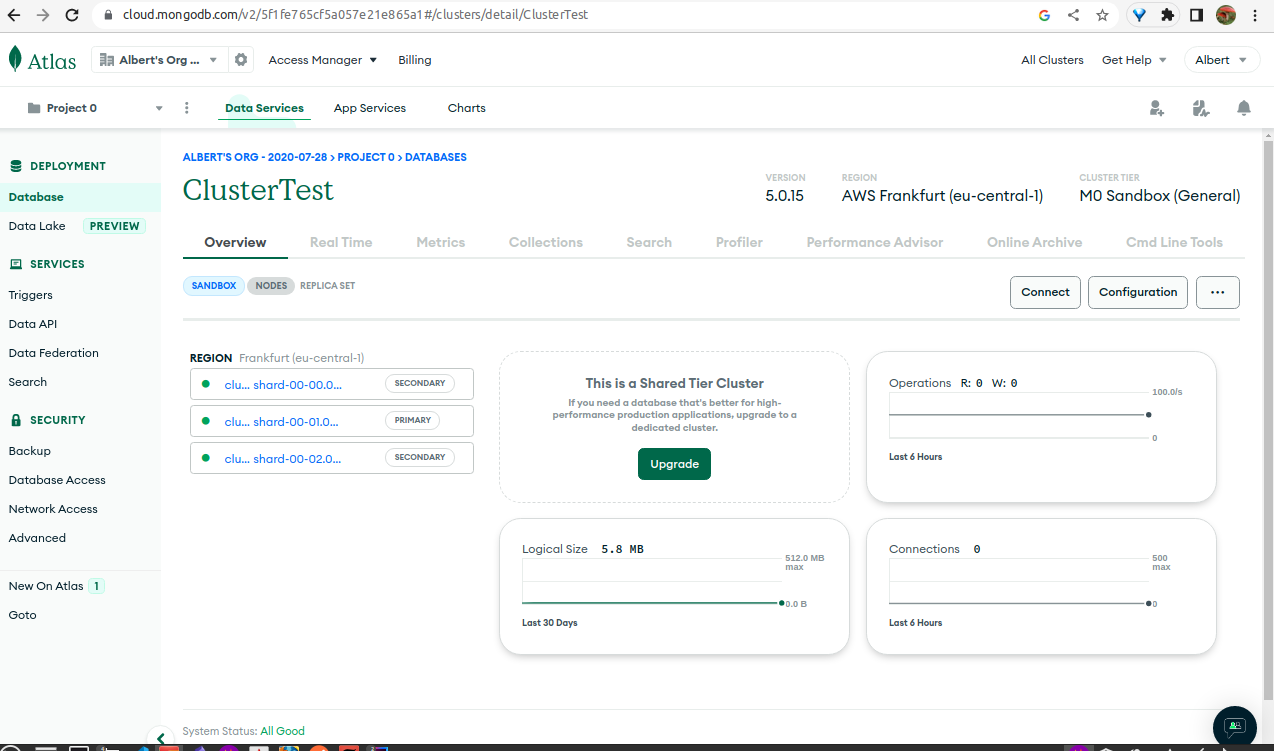
Create a new cluster: In the project dashboard, click on the “Build a New Cluster” button. Choose a provider, region, and the cluster tier that suits your requirements. Configure your cluster and click “Create Cluster” to start building your cluster.
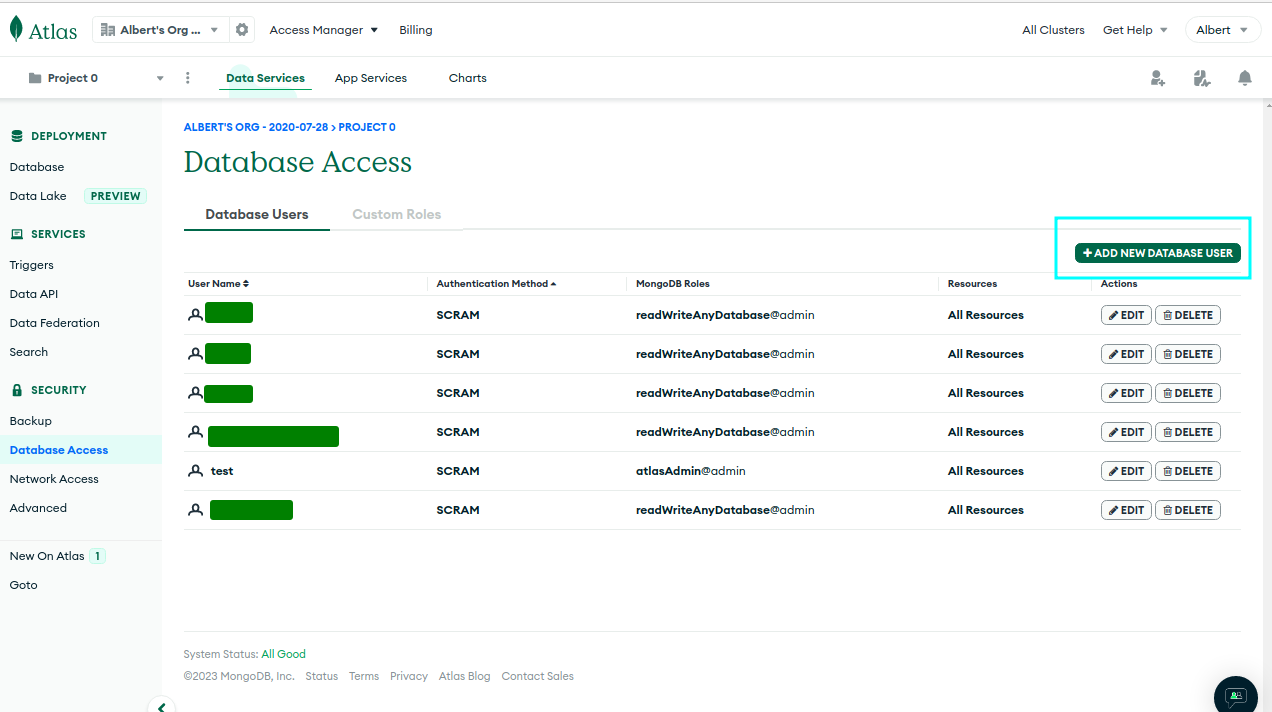
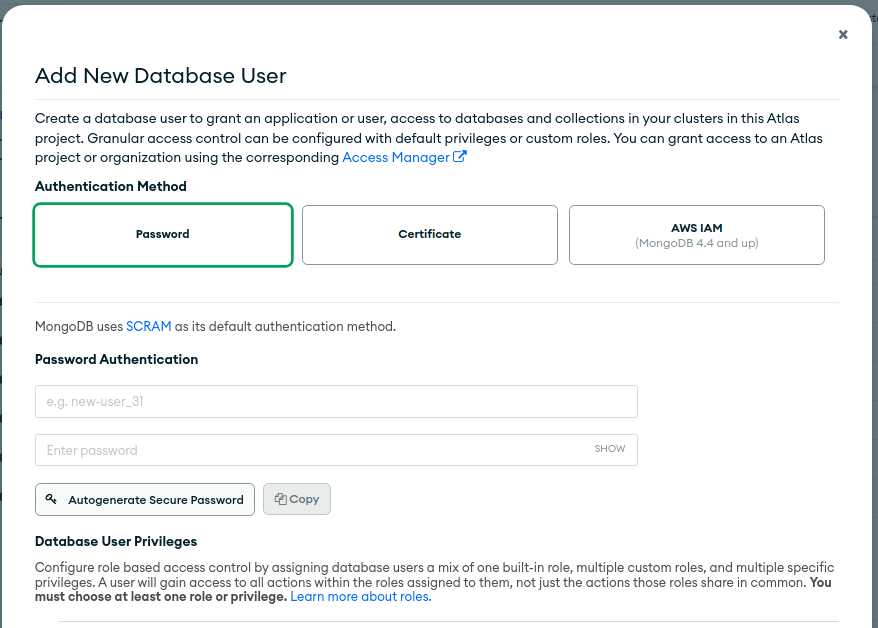
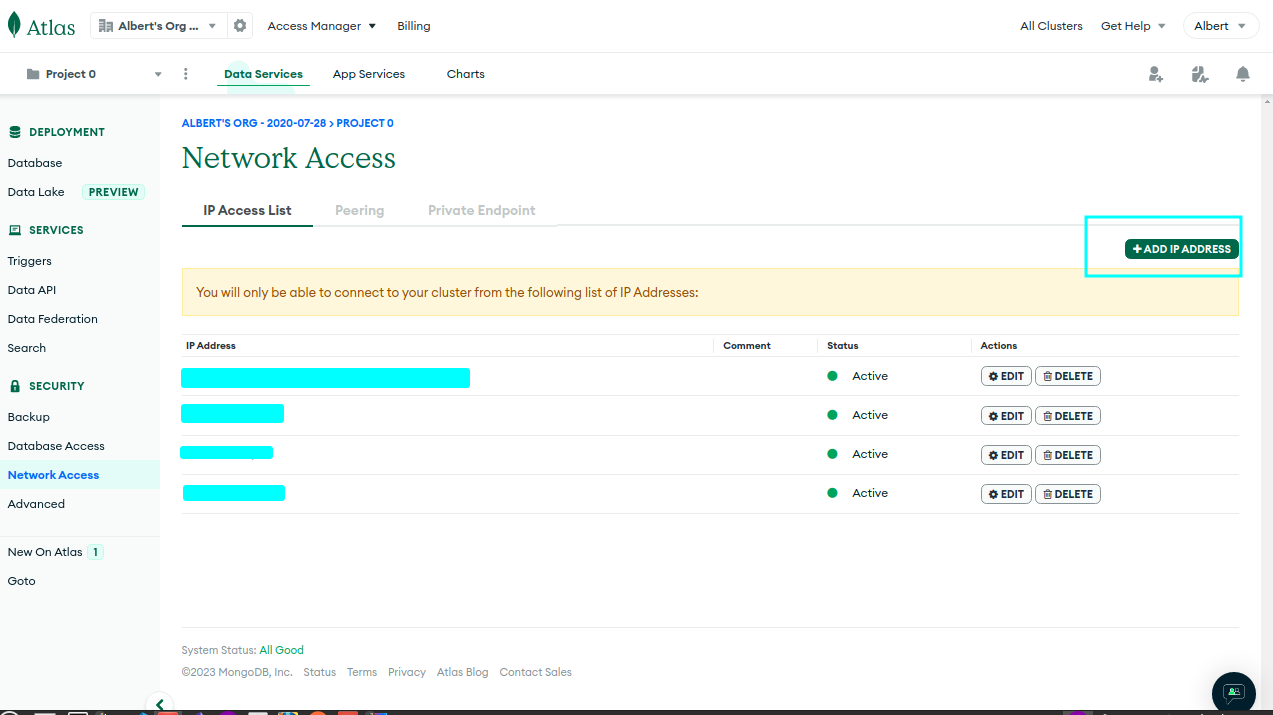
Create a database user and IP permission: Once the cluster is ready, create a database user with appropriate permissions and give network access (add your IP to
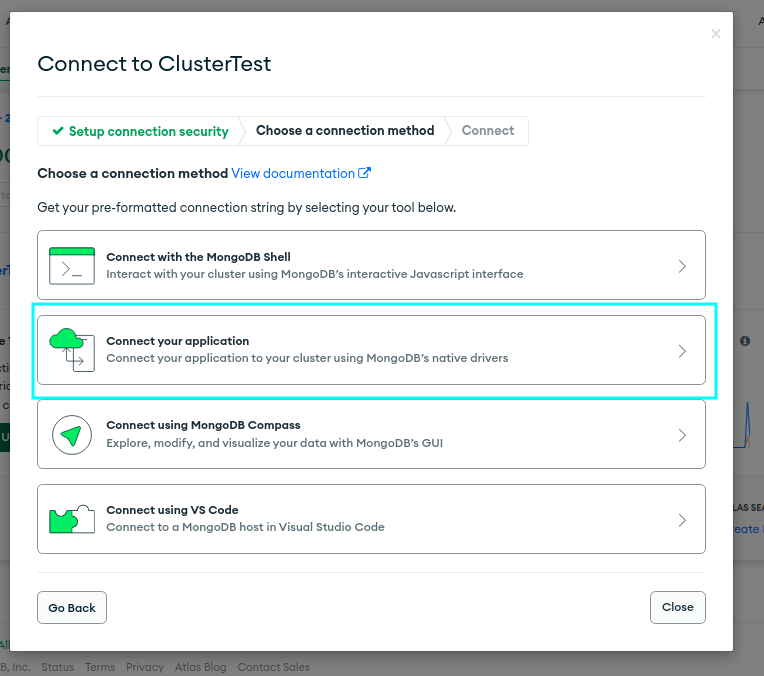
IP Access List).Get connection string: After creating a database user, you will get a connection string that you can use to connect to your MongoDB Atlas cluster. Copy the connection string to use it later.
Add MongoDB
dependency: In your Spring Boot project, add the MongoDBdependencyin thepom.xmlfile:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>- Configure
application.properties: In theapplication.propertiesfile, add the following properties:
spring.data.mongodb.uri=mongodb+srv://<username>:<password>@<clustername>.mongodb.net/<dbname>?retryWrites=true&w=majority
spring.data.mongodb.database=<dbname>Replace <username>, <password>, <clustername>, and <dbname> with your own values.
- Create
BookDocument: Create aBookDocumentclass with annotations.
@Document(collection = "books")
public class Book {
@Id
private String id;
private String title;
private String author;
// getters and setters
}- Create a
Bookrepository: Create a repository interface that extendsMongoRepository<Book, String>:
- Use the
Bookrepository: You can use theBookrepositoryto perform CRUD operations on your books collection.
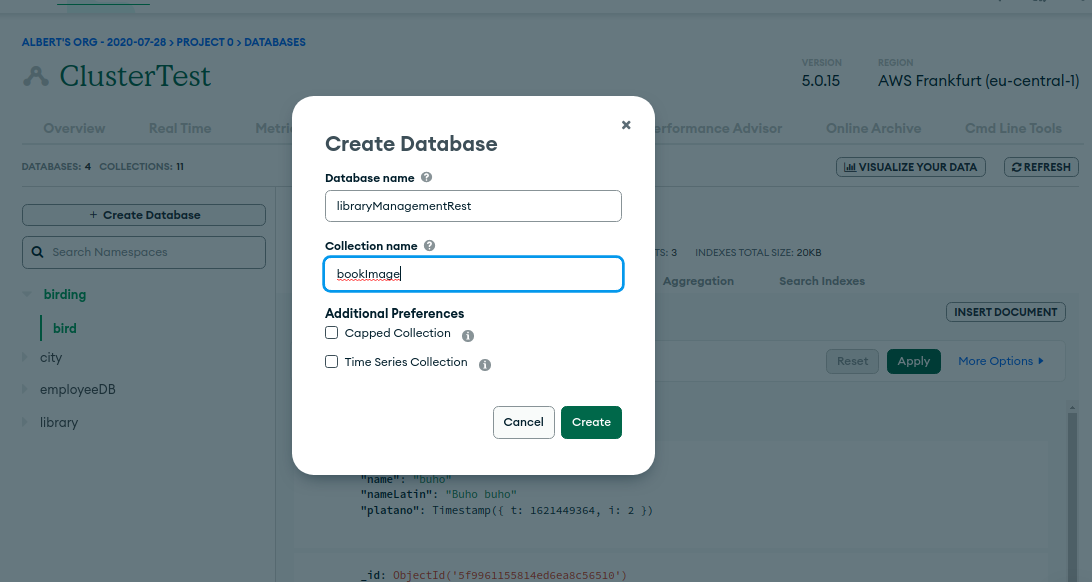
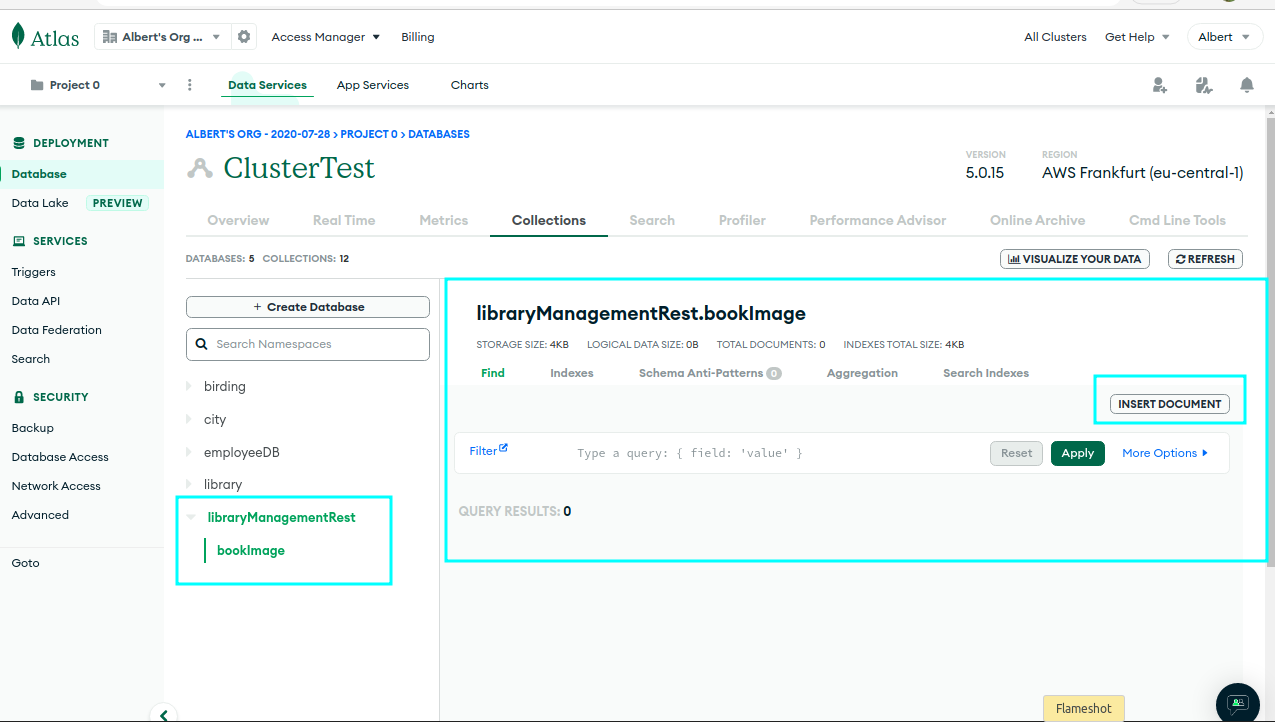
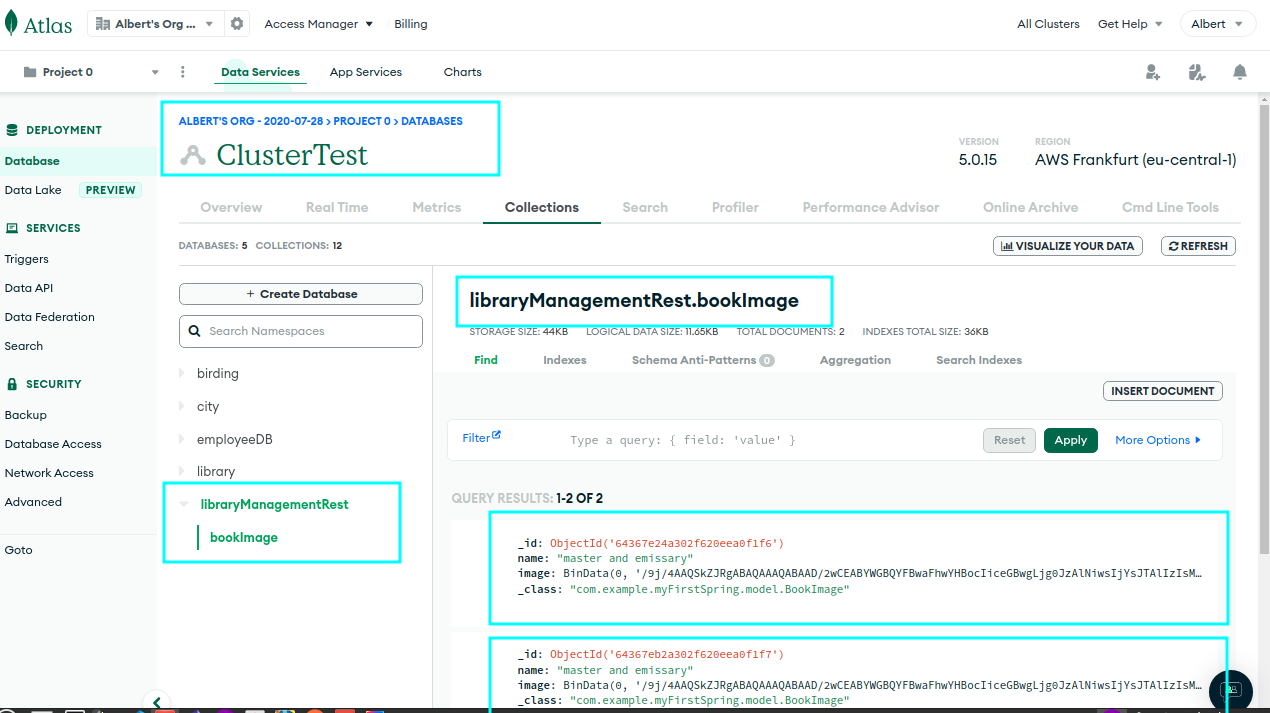
3 LibraryManagementRest: mongoDB
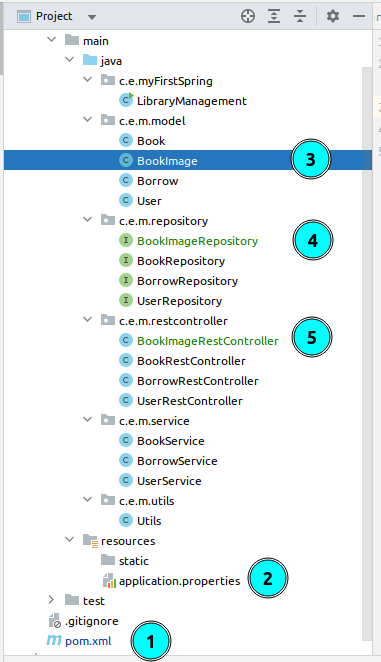
3.1 folder-tree
3.2 mongoDB: string connection
3.3 application.properties
To connect a Spring Boot application to MongoDB, you can use the spring.data.mongodb.uri property in the application.properties file to specify the connection string.
The connection string typically consists of the username, password, host, port, and database name.
spring.data.mongodb.uri=mongodb+srv://cifo:1234@clustertest.0h8fd.mongodb.net/LibraryManagementRest
spring.data.mongodb.database=LibraryManagementRestYou can also use a connection string with additional options like SSL, authentication mechanisms, and connection pooling. By placing the connection string in the application.properties file, you can easily configure the connection and change it without modifying the source code.
The Spring Boot MongoDB starter will automatically use the connection string to create a MongoDB client and configure the data source.
3.4 @Document
3.5 @RestController
@RestController
@RequestMapping("api/image")
public class BookImageRestController {
@Autowired
BookImageRepository bookImageRepository;
@PostMapping("upload")
public BookImage saveBookImage( @RequestParam String name, @RequestParam MultipartFile file) throws IOException {
BookImage bookImage = new BookImage();
//bookImage.setId(Utils.createUUID());
bookImage.setName(name);
bookImage.setImage( new Binary(file.getBytes() ));
bookImageRepository.save(bookImage);
return bookImage;
}
@GetMapping("/getData")
public String getDataBookImage(@RequestParam String id){
Optional<BookImage> bookImage = bookImageRepository.findById(id);
Encoder encoder = Base64.getEncoder();
return encoder.encodeToString( bookImage.get().getImage().getData() );
}
@GetMapping("/getImage")
public ResponseEntity<byte[]> getBookImage(@RequestParam String id){
Optional<BookImage> bookImage = bookImageRepository.findById(id);
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.IMAGE_JPEG);
return new ResponseEntity<>( bookImage.get().getImage().getData(), headers, HttpStatus.OK );
}
}3.6 @Repository
4 API Rest: postman
4.1 upload
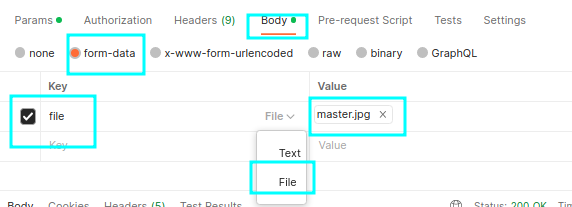
- Open Postman and create a new request.
- Set the HTTP method to
"POST"and set the request URL to"http://localhost:8090/api/image/upload". - Click on the “Body” tab and select the “form-data” radio button. Set the request body to the following key-value:
and the name of the image:
- This will create a new bookImage document, so click on the “Send” button to send the
request. - If the
requestis successful, you should receive a response with a status code of 201 Created and the bookImage document in the response body.
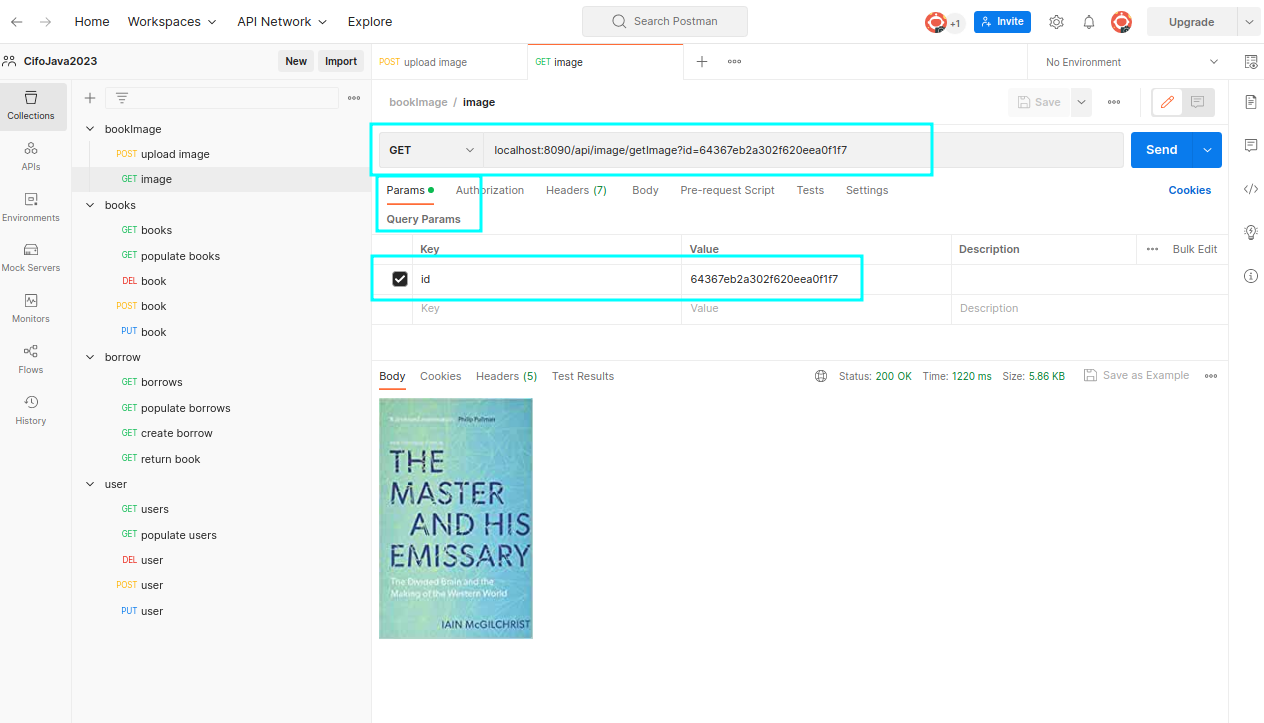
4.2 getImage
- Open Postman and create a new request.
- Set the HTTP method to
"GET"and set the request URL to"http://localhost:8090/api/image/getImage". - Click on the “Params” tab and select the “key-value” data:
id: 64367eb2a302f620eea0f1f7 - The response from the server:
4.3 upload one-to-many Book-BookImage
We are going to update upload method: both classes, Book and BookImage will share ids in a one-to-many relationship.
Bookwill be stored at local H2 SQL DB.BookImagewill be stores at MongoDB Cloud noSQL DB.
The below code is designed to:
- retrieve a book by its ID from a book repository.
- It then checks if the book exists and sets the book ID for a book image.
- If the book exists, it saves the book image to the book image repository and adds the book image ID to the book’s list of image IDs,
- and then saves the updated book.
method Create CRUD API Rest public BookImage saveBookImage() on @RestController public class BookImageRestController{}:
// Finds a book in the book repository by its ID, if present.
Optional<Book> book = bookRepository.findById(bookId);
// Checks if the book exists and sets the book ID for the book image.
if (book.isPresent()) bookImage.setBookId(book.get().getBookId());
// If the book doesn't exist, return null.
else return null;
// Saves the book image to the book image repository.
BookImage bookImageSaved = bookImageRepository.save(bookImage);
// Adds the book image ID to the book's list of image IDs and saves the updated book.
Book bookUpdated = book.get().addBookImageId(bookImageSaved.getId());
bookRepository.save(bookUpdated);- Open Postman and create a new request.
- Set the HTTP method to
"POST"and set the request URL to"http://localhost:8090/api/image/upload". - Click on the “Body” tab and select the “form-data” radio button. Set the request body to the following key-value for both,
nameandbookId:
5 Versions
endpoint example: http://localhost:8090/api/image/upload
| Code Version | Commit | Folder-Tree | Screeshoots |
|---|---|---|---|
| Library Management Rest MongoDB 0.0 | add MongoDB to project: application.properties, @Document, @Repository, POM BookImageRestController: upload, getImage, getDataImage |
Folder-tree bookImage |
- |
| Library Management Rest MongoDB 0.1 | all CRUD operations with bookImage document |
- | - |
| Library Management Rest MongoDB 0.2 | add ImageBook Id to books List book entity and bookId to imageBook document |
- | 1 - 2 |
| add data encryptation | - | - |
5.1 Postman apis
| Domain | Link | Objects |
|---|---|---|
| books | postman link | book |
| borrow | postman link | borrow |
| user | postman link | user |
| bookImage | postman link | bookImage |