React JS: Components
ReactJS Components
1 Overview
📘 Components
Components are one of the core concepts of React. They are the foundation upon which you build user interfaces UI.
2 COP: Components-Oriented Paradigm
COP, or Components-Oriented Paradigm, is a software design approach that emphasizes the use of reusable, modular components to build complex applications. In this paradigm, an application is typically divided into smaller, independent components that can be easily composed and reused.
The components-oriented paradigm is often associated with modern front-end JavaScript frameworks, such as React, Angular, and Vue.js, which provide tools and libraries for building applications using a component-based approach. However, the principles of COP can be applied to other programming languages and paradigms as well.
One of the main benefits of the components-oriented paradigm is that it helps to improve the maintainability and scalability of an application. By encapsulating functionality into discrete, reusable components, it becomes easier to modify and extend the application over time.
Additionally, the use of standardized, modular components can make it easier to build larger applications by allowing developers to reuse and compose components rather than building everything from scratch.
React is a JavaScript library for rendering user interfaces (UI).
UI is built from small units like buttons, text, and images.
React lets you combine them into reusable, nestable components. From web sites to phone apps, everything on the screen can be broken down into components.
3 Defining a component
React puts interactivity first while still using the same technology: a React component is a JavaScript function that you can sprinkle with markup.
profile.jsx
- Export the component: the
export defaultprefix is a standard JavaScript syntax (not specific to React). It lets you mark the main function in a file so that you can later import it from other files. - Define the function: with function
Profile() { }you define a JavaScript function with the nameProfile. - Add markup: the component returns an
<img />tag with src and alt attributes.<img />is written likeHTML, but it is actually JavaScript under the hood!
4 Using a component
For example, you can export a Gallery component that uses multiple Profile components:
profile.jsx
function Profile() {
return (
<img
src="https://i.imgur.com/MK3eW3As.jpg"
alt="Katherine Johnson"
/>
);
}
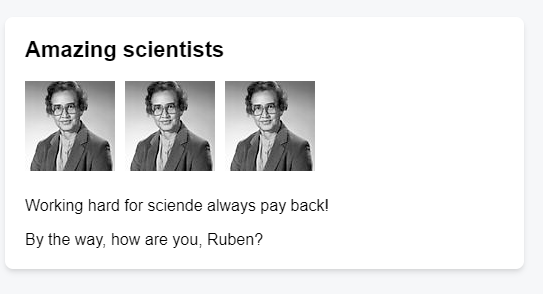
export default function Gallery() {
return (
<section>
<h1>Amazing scientists</h1>
<Profile />
<Profile />
<Profile />
<p>Working hard for sciende always pay back!</p>
<p>By the way, how are you, Ruben?</p>
</section>
);
}There are two primary ways to export values with
JavaScript:
defaultexports- and
namedexports.So far, our examples have only used
defaultexports. But you can use one or both of them in the same file. A file can have no more than one default export, but it can have as many named exports as you like.
5 Writing a component
5.1 Option#1: export default function BookList() {}
This option uses the function declaration syntax to define the BookList component and immediately exports it as the default export. This syntax is more familiar to developers who have experience with ES6 modules.
5.2 Option#2: const BookList = () => {}
This option uses the arrow function syntax to define the BookList component as a constant. Arrow functions have a concise syntax and can automatically bind this to the current scope, which can be helpful when working with React components.
5.3 Option#3: function BookList() {} export default BookList;
This option uses a function declaration to define the BookList component and then exports it as the default export on a separate line. This syntax is similar to option 1, but separates the function declaration from the export statement.
function BookList() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Book List</h1>
<ul>
<li>Book 1</li>
<li>Book 2</li>
<li>Book 3</li>
</ul>
</div>
);
}
export default BookList;In terms of behavior, all three options will create a function that can be used as a React component. However, the arrow function syntax in option 2 may provide some additional benefits in terms of performance and readability, especially for smaller components.
5.4 export default
In JavaScript, export is a keyword used to export functions, objects, or values from one module so that they can be used in another module.
When a module exports a function or object using the export keyword, it can be imported in another module using the import keyword.
The default keyword, when used with the export keyword, allows a module to export only one item as the “default” export.
This means that when another module imports from this module without specifying a specific import name, it will receive the default exported item.
The BookList function is being exported as the default export of the module.
This means that if another module imports from this module without specifying a specific import name, it will receive the BookList function as the default exported item.