Java SE: Maven
Maven and Java
📘 Dependency Management: Maven
Apache Maven is a software project management and comprehension tool. Based on the concept of a project object model (POM), Maven can manage a project’s build, reporting and documentation from a central piece of information.
These tools allow developers to specify the dependencies for their project in a file, and then automatically handle the process of downloading and installing those dependencies. This can save a lot of time and effort for developers, and helps ensure that all of the necessary dependencies are present and up-to-date in a project.
1 Maven
Maven is a build automation tool used primarily for Java projects.
Maven can also be used to build and manage projects written in C#, Ruby, Scala, and other languages. The Maven project is hosted by the Apache Software Foundation, where it was formerly part of the Jakarta Project.
Maven addresses two aspects of building software: - how software is built and - its dependencies
1.1 Maven Central Repository
Link: Maven Central Repository
Maven repository is a directory where all the dependencies such as jars, library files, plugins, or other artifacts that will be required by the projects are stored.
These repositories help us to store and maintain useful resources so that they can be used in our maven projects while building and deploying the artifacts.
All the layout and structure of the underlying repositories of maven of any type are completely hidden for maven users.
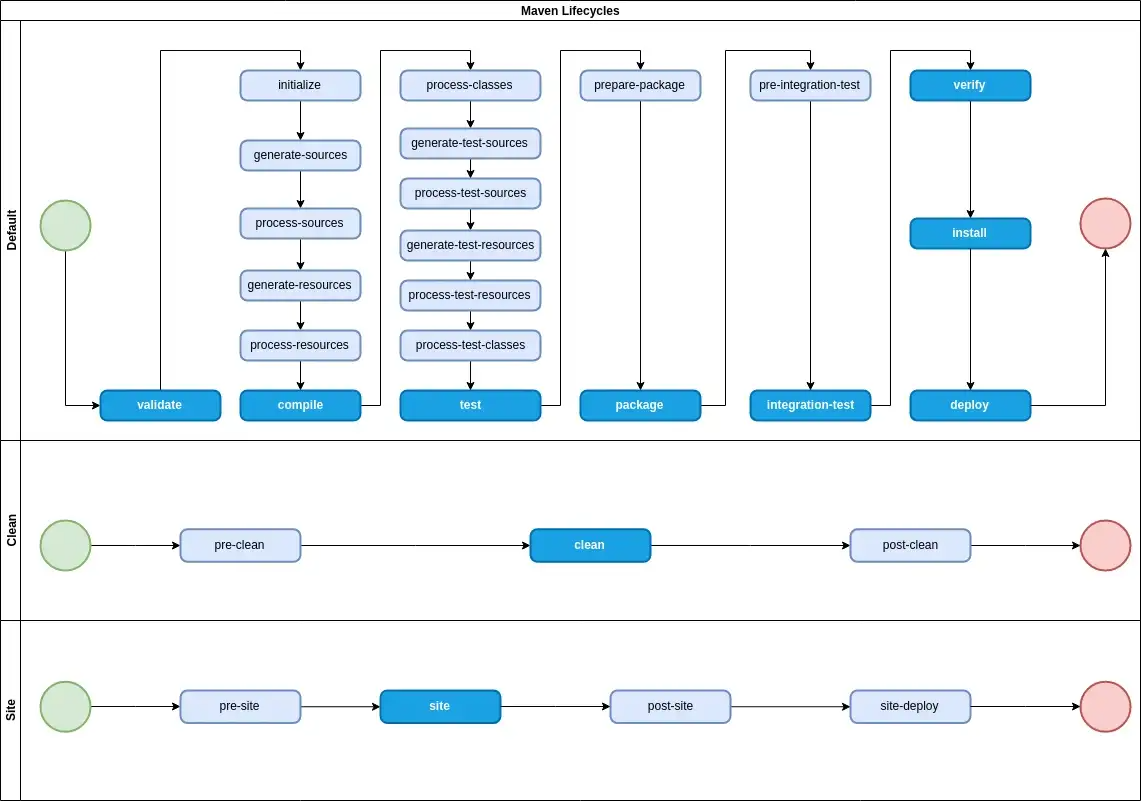
1.2 Maven Lifecycle
Maven is a build automation tool for Java projects. It is used to manage the build, reporting, and documentation of a project. Maven has a defined lifecycle that outlines the steps required to build and distribute a project.
The Maven lifecycle has three main phases:
clean: This phase is used to clean up any previous build artifacts.default: This is the main phase of the lifecycle, where the project is built, tested, and packaged.site: This phase is used to generate the project’s documentation and site information.
Each phase of the Maven lifecycle consists of a set of build phases, which are executed in a specific order.
For example, the default phase consists of the following build phases:
Each build phase consists of a set of build goals, which are the specific tasks that are executed to accomplish the phase’s objectives. For example, the compile phase has a build goal called compiler:compile that is responsible for compiling the project’s source code.
validate: Validate the project’s configuration and dependencies.compile: Compile the project’s source code.test: Run the project’s tests.package: Package the compiled code into a distributable format (e.g., a JAR file).install: Install the packaged code into the local repository.deploy: Deploy the packaged code to a remote repository for others to use.
By following the defined Maven lifecycle, developers can easily build, test, and distribute their Java projects in a consistent and repeatable manner.
2 Dependencies, plug-in & library
In Maven projects, the terms “plugin,” “dependency,” and “library” refer to different concepts related to project configuration, build processes, and external dependencies.
Plug-in
- A Maven plugin is a set of goals (tasks) and configurations that can be executed within the Maven build lifecycle.
- Plugins extend or modify the behavior of the Maven build process. They can perform tasks such as compiling code, packaging artifacts, running tests, generating documentation, and more.
- Plugins are specified in the
section of the project’s pom.xmlfile. They are responsible for executing various build-related tasks during different phases of the build lifecycle.
Example of a Maven plugin configuration in pom.xml:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.0</version>
<configuration>
<!-- Plugin configuration options go here -->
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>Dependency
- A Maven dependency is an external library or module that your project relies on.
- Dependencies are specified in the
section of the project’s pom.xmlfile. Maven will automatically download and manage these dependencies from a central repository during the build process. - Dependencies can include libraries, frameworks, and other artifacts that your project needs to compile, run, or test.
Example of a Maven dependency configuration in pom.xml:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>example-library</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>Library
- In the context of Maven, a library is a collection of pre-compiled code and resources that provide specific functionality.
- Libraries are typically packaged as JAR (Java Archive) files and are distributed through Maven repositories.
- When you declare a dependency on a library in your project’s
pom.xml, Maven will download and include the necessary JAR files during the build process.
Example of a library dependency in pom.xml
3 Configurations in idea ide
3.1 JDK, SKD and language level
In a Maven IntelliJ IDEA project, the SDK (Software Development Kit) represents the Java version used for compilation and execution, determining the available libraries and features. The language level, on the other hand, specifies the language features and syntax level within that SDK.
While the SDK sets the overall compatibility, the language level refines language-specific settings.
For example, using JDK 11 as the SDK with language level 8 means leveraging JDK 11 capabilities while restricting language features to those compatible with Java 8 syntax.
Proper alignment between SDK and language level ensures both Java version compatibility and language feature availability.
SDK, JDK, JRE
SDK (Software Development Kit) is a broader term encompassing tools and libraries for software development.
JDK (Java Development Kit) specifically refers to the Java SDK, providing tools and resources for Java development, including the Java Runtime Environment (JRE), compiler, and libraries.
3.2 Archetype, GroupId, ArtifactId
An archetype is a template for a project. It provides a predefined structure and files for a project, so that you don’t have to create them manually.
GroupId and artifactId are two important elements of a Maven project.
- The groupId is a unique identifier for a project, and is typically used to group related projects together.
- The artifactId is the unique identifier for a specific project, and is used to identify the project within the group.
Together, the groupId and artifactId help to uniquely identify a project within the Maven ecosystem.