Linux Lab#LI02-1: Export env user with grep and pipe
Lab
📘 Linux Lab#LI02-1: Export env user with grep and pipe
Export the environment of a user linux account from user’s account with root privileges on OpenSUSE bash (or Linux Mint).
1 CLI tools
1.0.1 sudo: su - root -c
To run a single command as the root user. The -c option is used with the su command to specify a command that should be run as the target user.
1.0.2 redirect: >>
The > symbol is used for output redirection. Here the output of command ls -al is re-directed to file listings instead of your screen.
The >> operator is used to redirect the output of a command to a file, and append the output to the end of the file.
iconfig /all > networksettings.txt 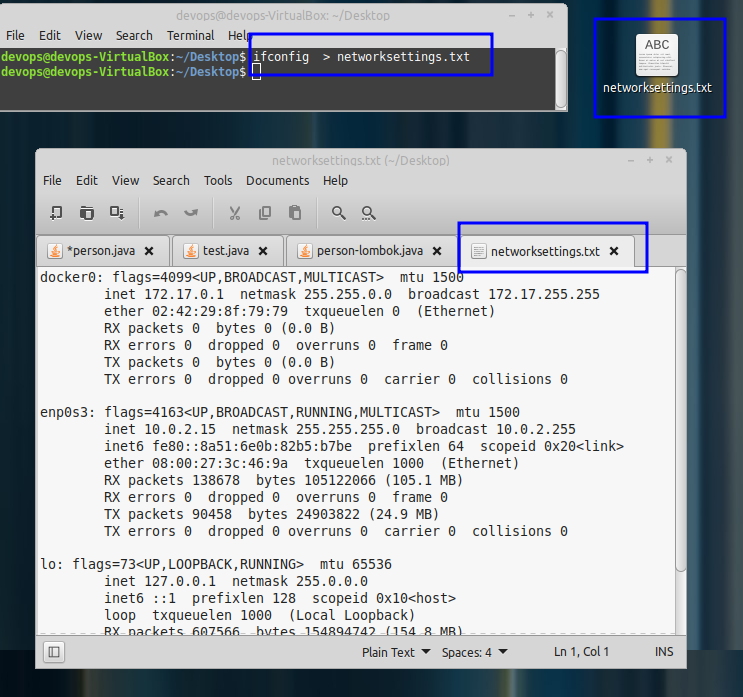
ping 8.8.8.8 > 'C:\Users\devops\Desktop\PingResults.txt' 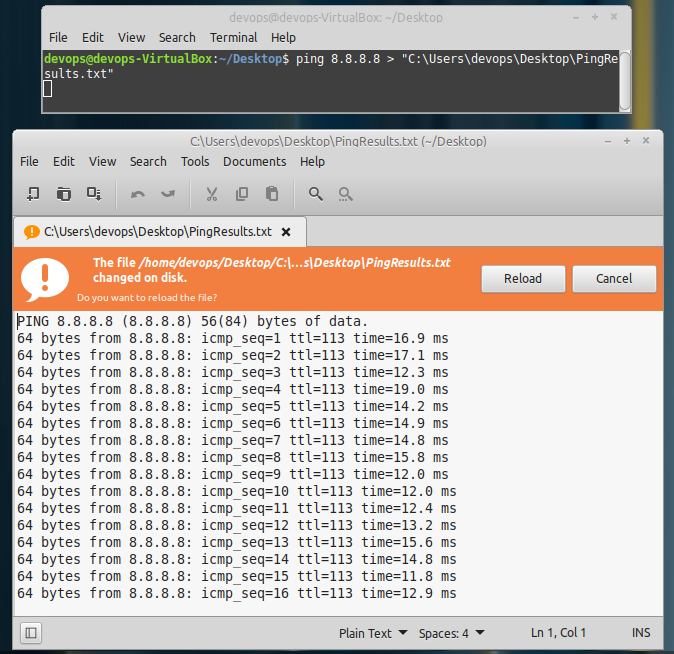
1.0.3 grep: grep -v
The -v option is used with the grep command to invert the sense of matching. When used, grep will display lines that do not match the given pattern.
1.1 environment: env
The env command is a built-in command in Linux and Unix-like operating systems that is used to display or set environment variables.
Environment variables are named values that can be used to store information about the system or the user. They are used to configure the shell and to set options that affect the behavior of the system and programs.
env 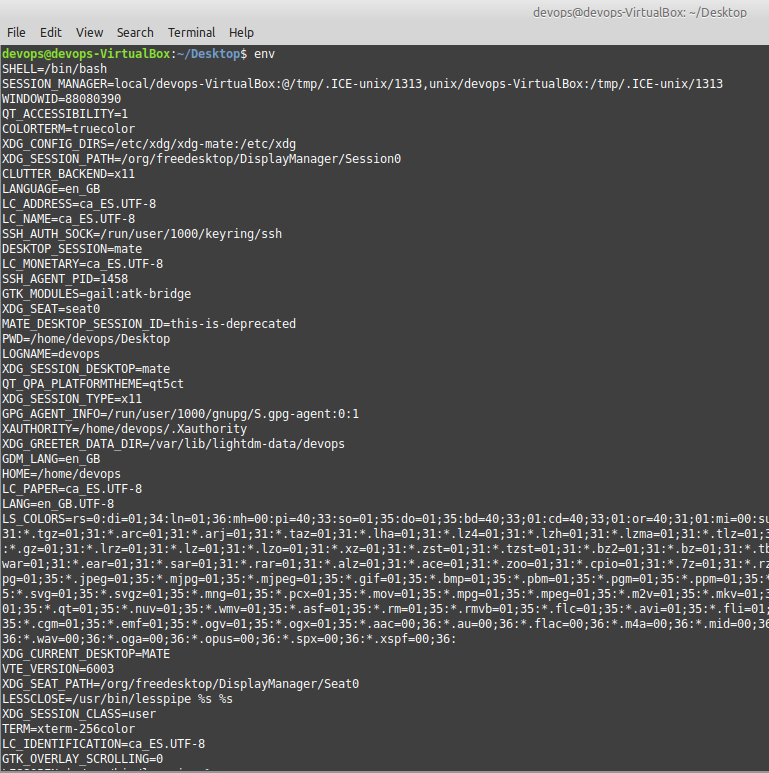
1.2 set: set +a
The set builtin command is used to set options and/or positional parameters. The -a option is used to enable the export attribute for each name, which means that the corresponding variable will be exported with the export command to the environment of subsequently executed commands.
The + sign before the a option toggles the attribute off. This means that set +a disables the export attribute for the specified variables, and set -a enables it.
2 Solving discussion
We could do this:
This will run a subshell as the root user, source the current user’s .bashrc file to set up the environment, and then export the environment variables to /etc/environment. In Bash, the set builtin command is used to set options and/or positional parameters. The -a option is used to enable the “export” attribute for each name, which means that the corresponding variable will be exported with the export command to the environment of subsequently executed commands.
The + sign before the a option toggles the attribute off. This means that set +a disables the “export” attribute for the specified variables, and set -a enables it.
su - root -c 'bash -c "set -a; source ~/.bashrc; set +a; env | grep -v \"^USER_VARIABLE=\" >> /etc/environment"'su - root -c: This will allow you to run a command as the root user while preserving the environment of the current user.grepand>>: You will pipe the output togrepto filter out theUSER_VARIABLEvariable. The resulting output is then redirected to/etc/environmentusing>>.- This will add all of the environment variables from the current user’s environment to the
/etc/environmentfile, which is used to set the environment for all users on the system.
If you want to preserve the entire environment, including aliases, functions, and shell options, you can use the bash -c command instead: