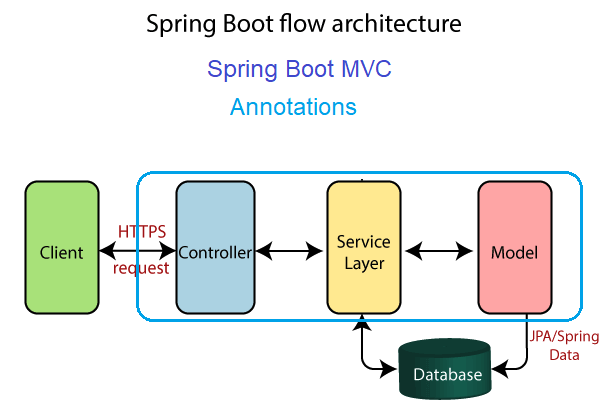
Spring Boot: Annotations
Spring Boot
📘 Annotations
In Spring Boot, annotations are used to configure and enable various features and functionality.
They are used to provide metadata about a class, method, or field, and are used by the Spring framework to determine how to handle that class, method, or field.
Here are some examples of common annotations used in Spring Boot:
1 App
@SpringBootApplication: This annotation is used to enable the default configuration of a Spring Boot application.- Basically, the
@SpringBootApplicationannotation is a combination of the following three Spring annotations:@Configuration,@EnableAutoConfigurationand@ComponentScan.
- Basically, the
2 Class
@Component: This annotation is used to automatically detect the component classes without any need to write any explicit code. Spring framework scans classes with@component, initialize them, and injects the required dependencies.@RestController: This annotation is used to define a class as a RESTful web service controller.@Controller: This annotation is used to define a class as a web service controller@Repository: This annotation is used to define a class as a JPA repository, which can be used to perform CRUD operations on a database.@Service: This annotation is used to define a class as a service class that defines the business logic.
3 Dependence Injection
@Autowired: This annotation is used to automatically wire a bean from the Spring application context into a class field or method. When we use this annotation Spring Boot is responsible to create the instance of that variable, it basically manages the whole life cycle of the object.
4 POJO, @Bean and @Entity
POJO (Plain Old Java Object)
A POJO is a simple Java object that doesn’t depend on any framework-specific interfaces or annotations.
@Bean
The @Bean annotation is used in Spring to declare a bean to be managed by the Spring container. It’s typically used in @Configuration classes.
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public User user() {
User user = new User();
user.setName("John");
user.setAge(30);
return user;
}
}@Entity
The @Entity annotation is used in JPA to mark a POJO as a persistent entity that will be mapped to a database table.
@Entity
@Table(name = "users")
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
private int age;
// Getters and setters
}In summary:
POJO: A simple Java object@Bean: Declares a Spring-managed bean@Entity: Marks a class for ORM persistence
These concepts are fundamental to Spring and JPA, providing flexibility in object management and persistence[1][2].
Citations: [1] https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/reference/core/beans/java/bean-annotation.html [2] https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/spring-bean-annotation
4.1 @Bean
@Bean in Spring is:
- A method-level annotation
- Used to declare a Spring
beantypically used in@Configurationclasses - Tells Spring to:
- manage the object returned by the method
- and allows you to configure and customize the bean
- JavaBeans - Wikipedia
@Beanin Spring is like telling a toy factory to make a special toy for you. When you use@Bean, you are saying,:
- “Please create this toy and keep it safe so I can play with it whenever I want.”
Just like the factory remembers how to make your favorite toy, Spring remembers how to create and manage the special object you asked for, so you can use it in your game whenever you need it.
Example:
5 JPA
@Entity: This annotation is used to define a class as a JPA entity, which can be used to interact with a database.
5.1 Mapping and parameters
@RequestMapping: This annotation is used to map HTTP requests to specific methods in a controller class.@RequestParam: This annotation is used to bind request parameters to a method parameter in the controller.
@PathVariable: This annotations binds the placeholder from the URI to the method parameter and can be used when the URI is dynamically created or the value of the URI itself acts as a parameter.
5.2 @Component
The @Component annotation is used to mark a class as a Spring-managed component.
- Automatic
BeanCreation:@Componenttells Spring to automatically create and manage an instance of the annotated class as a bean in the application context. - Dependency Injection: It enables the class to be a candidate for dependency injection, allowing Spring to automatically wire its dependencies.
- Component Scanning:
@Componentworks with Spring’s component scanning feature to detect and register beans without explicit configuration.
How @Component Works:
- Class-Level Annotation:
@Componentis applied at the class level. BeanCreation: When Spring scans the classpath, it detects classes annotated with@Componentand creates beans for them[1][2].- Default Naming: By default, the bean name is the class name with the first letter in lowercase.
- Customizable: You can specify a custom name for the bean using
@Component(“customName”). - Specialized Annotations:
@Service,@Repository, and@Controllerare specialized forms of@Componentfor specific use cases.
5.3 Usage Example
In this example, Spring will automatically create a bean of MathComponent, which can then be autowired or retrieved from the application context.
Benefits
By using @Component, we can leverage Spring’s dependency injection and inversion of control features with minimal configuration, leading to more maintainable and modular code.
- Simplifies Configuration: Reduces the need for XML-based bean definitions.
- Promotes Loose Coupling: Facilitates dependency injection and easier unit testing.
- Improves Code Organization: Helps in categorizing classes based on their roles in the application.
5.4 @Transient
The @Transient annotation is used in Java persistence contexts, particularly with JPA (Java Persistence API) and frameworks like Hibernate. It indicates that a field should not be persisted to the database.
Usage of @Transient
@Transient is applied to fields or properties in an entity class that you don’t want to be stored in the database. This is useful for:
- Calculated fields
- Temporary data
- Fields used only in application logic
Code Example
@Entity
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
@Transient
private String fullName;
public String getFullName() {
if (fullName == null) {
fullName = firstName + " " + lastName;
}
return fullName;
}
// Other getters and setters
}In this example, fullName is marked as @Transient because it’s a calculated field based on firstName and lastName. It won’t be stored in the database but can be used in application logic.
Remember, @Transient fields:
- Are not persisted to the database
- Are not included in database operations (insert, update, select)
- Can still be used within the application
@Transientprovides flexibility in managing which data is stored persistently and which is used only in-memory.
5.5 @Transactional
The @Transactional annotation is used in Spring to manage database transactions declaratively. It ensures that a group of operations are executed as a single, atomic unit of work.
Key Features of @Transactional
- Automatic transaction management
- Rollback on exceptions
- Configurable isolation levels and propagation behaviors
Usage Example
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Transactional
public void createUser(User user) {
userRepository.save(user);
// If any exception occurs after this point, the save will be rolled back
sendWelcomeEmail(user);
}
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public User getUser(Long id) {
return userRepository.findById(id).orElse(null);
}
}Key Points
@Transactionalcan be applied at class or method level- By default, it rolls back on
RuntimeExceptions readOnly= true optimizes read operations- Can be customized with attributes like:
- propagation
- isolation
- timeout
rollbackFor/noRollbackFor
Benefits
- Simplifies transaction management
- Promotes clean, modular code
- Improves data integrity and consistency
@Transactionalis a powerful tool in Spring for ensuring data consistency and managing complex database operations with minimal boilerplate code.